Fresno State Transportation Institute
Projects
FSTI Project Booklet
Year 8 (2025)
PI's Background: Dr. Yushin Ahn
Project's date: December, 2025
Abstract: This project evaluates flood risks to transportation infrastructure in Fresno City through the integration of high resolution Airborne Laser Scanning and Geographic Information Systems. The study identifies vulnerable roads, bridges, and drainage systems, simulates flood scenarios, and develops actionable mitigation strategies. By combining precise elevation data with advanced hydrological and hydraulic modeling, the project produces a GIS-based decision support tool to improve flood resilience and transportation planning.
Fresno County faces ongoing flood challenges due to its geography, urban development, and seasonal snowmelt from the Sierra Nevada. These factors increase the likelihood of road closures and infrastructure damage, disrupting public safety and economic activity. While regional flood assessments exist, this research focuses specifically on transportation infrastructure, addressing a gap in current planning efforts.
Key outcomes include flood risk maps, recommendations for improved road and drainage design, and a tool for local agencies to prioritize investments. The results aim to enhance resilience in Fresno and serve as a model for other flood-prone regions.
Report Coming Soon
PI's Background: Dr. Fariborz M. Tehrani
Project's date: December, 2025
Abstract: This project investigates the stress strain behavior of structural lightweight aggregate concrete used in transportation infrastructure, with a focus on applications in high performance pavements and bridge decks. As advancements in design and construction continue, understanding the modulus of elasticity and stress strain relationship of lightweight concrete has become increasingly important for ensuring structural performance and durability. The research aims to establish stress strain models for lightweight concrete and assess their impact on the service life of critical infrastructure. It also includes a lifecycle analysis that quantifies environmental footprints such as greenhouse gas emissions associated with lightweight concrete bridge decks. This work aligns with current Federal Highway Administration priorities, including internally cured concrete performance enhancement and integration of environmental product declarations into project delivery. By contributing to updated empirical models and design practices promoted by AASHTO and other standards bodies, the project supports more accurate predictions of long-term material behavior and promotes sustainable and resilient infrastructure design.
Report Coming Soon
PI's Background: Dr. Josephine Hazelton-Boyle
Project's date: December, 2025
Abstract: This study examines how cities in California’s Central Valley are planning for intermodal and multimodal connectivity with the California High Speed Rail system, amid ongoing construction and public debate. As the first voter-approved high speed rail initiative in the United States, the project promises enhanced mobility and environmental benefits, yet faces criticism over local disruptions and uncertain long-term impacts. Focusing on a region shaped by automobile-centric planning, this research investigates how local jurisdictions are balancing economic, environmental, and community priorities while preparing for integration with the high speed rail system. Using a mixed methods approach that includes analysis of public planning documents and interviews with local officials, the project evaluates readiness for linking active transportation, public transit, and vehicle networks to rail stations. The findings will support recommendations to improve connectivity, equitable access, and station area planning. The study also highlights the evolving role of the public, particularly marginalized communities, and aims to inform future research on passenger rail implementation in politically and socially complex regions.
Report Coming Soon
PI's Background: Dr. Hovannes Kulhandjian
Project's date: December, 2025
Abstract: The SMART-TWIN project seeks to revolutionize transportation planning and operations through the development and deployment of Digital Twin (DT) technology. By creating dynamic, real-time virtual replicas of physical transportation systems, this project will enable predictive modeling, scenario testing, and data-driven decision-making to address challenges in traffic congestion, infrastructure management, and emergency response. Building upon global successes and aligning with national initiatives such as the USDOT Smart City Challenge, SMART-TWIN will develop scalable frameworks for implementing DTs in transportation, promoting safer, more efficient, and sustainable systems. Key outcomes include enhanced traffic flow, improved disaster responsiveness, reduced emissions, and optimized maintenance. The project also emphasizes workforce development by integrating AI, machine learning, IoT, and big data into research and training. Through practical implementation strategies and hands-on student involvement, SMART-TWIN prepares the next generation of engineers and planners to lead in the evolution of intelligent transportation infrastructure.
Report Coming Soon
PI's Background: Dr. Jaymin Kwon
Project's date: December, 2025
Abstract: The StarTraq 2025 project aims to advance environmental health equity by enhancing geospatial understanding of transportation-related air quality impacts in California’s San Joaquin Valley. Building upon the StarTraq 2024 geospatial time-series database, this initiative integrates newly analyzed epigenetic data from the Children’s Health and Air Pollution Study–San Joaquin Valley (CHAPS-SJV) to assess molecular-level health effects of prolonged exposure to traffic-related air pollutants. The project focuses on linking vehicle miles traveled, land use, and roadway networks with socio-economic and environmental exposure data to inform policies that promote active transportation modes and improve transit accessibility for all populations. By identifying elevated roadside concentrations of PM2.5, black carbon, and PAHs. The study highlights disproportionate risks to low-income and minority communities. StarTraq 2025 seeks to support collaborative research and evidence-based decision-making by expanding the integrated GIS database to capture complex relationships between mobility, pollution, infrastructure, and long-term health outcomes, with the ultimate goal of fostering healthier, more sustainable communities.
Report Coming Soon
PI's Background: Dr. Woonki Na
Project's date: December, 2025
Abstract: The increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous systems has underscored the need for more advanced and automated Battery Management Systems (BMS). This paper presents the objectives, background, and driving factors behind the development of an Automated BMS tailored for modern EV applications. The system aims to enhance battery performance and longevity by continuously managing the state of charge (SOC), state of health (SOH), and thermal conditions. It improves energy efficiency through intelligent power distribution, especially under high-demand autonomous driving scenarios. Safety is prioritized by integrating automated safeguards against overcharging, over-discharging, and thermal events. Furthermore, the system facilitates autonomous charging and energy optimization, supporting both vehicle operations and grid interaction. With rising global EV demand, increasing emphasis on autonomous mobility, and tightening regulatory standards, automated BMS offers a scalable, cost-effective solution for improving battery reliability, operational efficiency, and safety in next-generation electric mobility.
Report Coming Soon
Year 7 (2024)
PI's Background: Dr. Yushin Ahn
Project's date: December, 2024
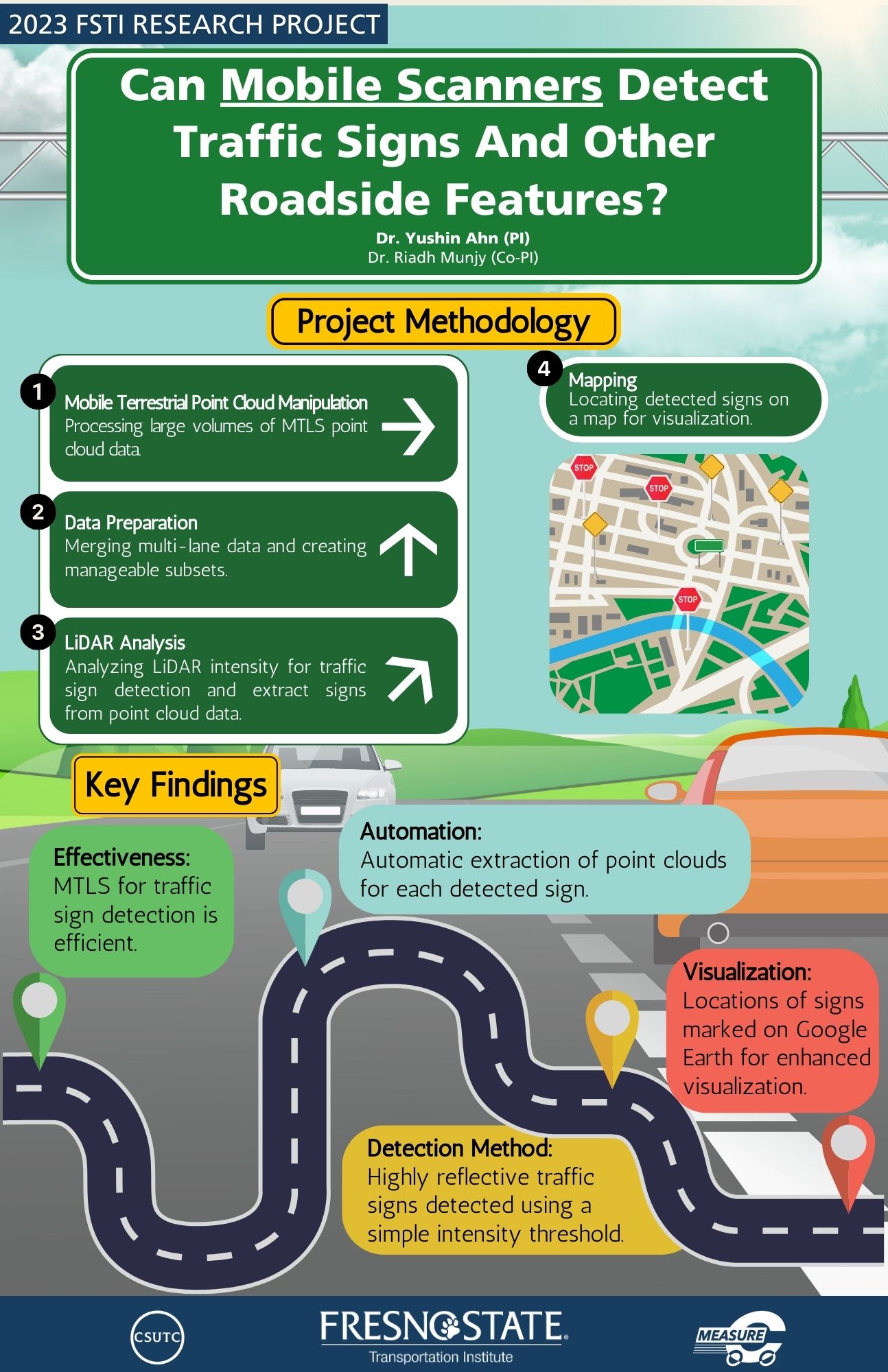
Abstract: Lately, numerous State transportation agencies have been incorporating Mobile Laser Scanning technologies into their operation. Integrated Mobile Laser Scanning with camera, GNSS and IMU, in the current terms, Mobile Terrestrial Laser Scanning (MTLS) yields comprehensive field data in the form of a point cloud. When applied on roadways, this technology enables the 3D visualization, identification, and extraction of various roadside assets, all facilitated by skilled operators.
From our prior FSTI project focused on traffic sign detection using Mobile LiDAR point cloud, we successfully obtained 8 miles' worth of MTLS data from the Caltrans Office of Land Surveyors and their contacts. Our findings demonstrated the detectability of traffic signs within the data, accurately positioning them on the map. Additionally, our research highlighted the potential of leveraging MTLS data for the enhanced detection of various roadside features, including concrete barriers, road markings, slopes, and more.. This study delves into three key aspects. Firstly, it explores the extraction of cross-sectional features like lane slope (or crown), and superelevation on horizontal curves. Secondly, it involves the assessment of road conditions, including profiling along the lanes and identifying damaged road sections. Lastly, the study explores the application of deep learning for point cloud classification in MTLS data.
PI's Background: Dr. Hovannes Kulhandjian
Project's date: December, 2024
Abstract: The scorching wildfires of 2017 and 2018 cast California into a devastating inferno, seizing national attention and leaving entire communities in ruins. The ferocious Thomas fire, tearing through Ventura and Santa Barbara Counties, and the relentless Tubbs fire, laying waste to Napa, Sonoma, and Lake Counties, unleashed destruction upon more than 7,200 structures and devoured a staggering 318,000 acres in 2017. Then, in 2018, the Woolsey fire's unforgiving blaze scarred 1,990 structures across nearly 97,000 acres in Los Angeles and Ventura Counties [1]. The state faced a historic wildfire season in 2020, including the August Complex Fire, which surpassed the Mendocino Complex as the largest recorded wildfire in California's history.
These wildfires not only resulted in substantial property damage and loss of life but also have severe environmental impacts, affecting air quality, wildlife, and ecosystems across the state. The scale and frequency of these wildfires highlight the urgency for innovative approaches in wildfire prevention, early detection, and efficient response strategies to mitigate future catastrophes.
Several research works have been conducted on wildfire detection, spread estimation, wildfire evacuation, search and rescue operations [2-5]. However, to the best of our knowledge there are no unified framework that tries to address several of those important issues simultaneously on a single framework. We are confident that implementing our proposed framework would significantly benefit wildfire control authorities.
PI's Background: Dr. Jaymin Kwon
Project's date: December, 2024
Abstract: The main objective of the StarTraq 2024 project is to create safer communities and provide greater opportunities for the promotion of active transportation modes such as biking and walking, increasing access to transit. Through research on spatio-temporal analyses of roadside transportation-related air quality, people of all abilities and socioeconomic levels can enjoy the accessibility of transit and choices of healthier transit to improve their quality of life. The study aims to provide public information on transportation-related environmental exposure in a timely and relevant so that people can use the knowledge for decision-making of design and application of new materials and technologies to improve the public health of Californians. The proposed StarTraq 2024 project will construct the geospatial time-series database that connects and illustrates the historical changes in air quality impacted by transportation-related air pollutants (TRAPs), commercial/private vehicle miles traveled (VMT), roadway infrastructure network/land use in urban and rural areas, regional socio- economic data, and human disease and health data.
Report Coming Soon
PI's Background: Dr. Jorge Pesantez
Project's date: December, 2024
Abstract: The main objective of this project is to develop and apply a predictive model to forecast traffic congestion events using deep neural network architectures. Based on a predictive model that reports future traffic conditions using public data sets, the project goal is to provide an effective model to city planners and transit agencies for enhancing planning and management activities. This proposed project encompasses the objective by developing an effective tool to optimize passenger and freight movements with innovative data models and advanced congestions management tools.
Report Coming Soon
PI's Background: Professor Holly Sowles
Project's date: December, 2024
Abstract: As a continuation from Fall 2023, the Intelligent Interior Design Visualization Lab proposes to complete the design development of the remaining four bike shelters for the Fresno City Bike Campus Project. Additionally, the Vis Lab will create a heat island toolkit which is a framework to analyze multiple design strategies that mitigate extreme temperatures on surfaces. We will continue creating complementary bike shelters that act as backdrops to the Scribbles Bike Sculptures while complementing the local district's architectural aesthetics. Each design outcome offers shade, charging stations, water access, and bike repair facilities. The heat island toolkit will analyze and attempt to reduce extreme temperatures on the pathways and at the trailheads of the Fresno City Bike Campus. After developing the toolkit, we will engage local districts in a democratized design process to gather local design preferences for community placemaking. After determining the preferred toolkit for each district, we will 3D print modular prototypes of both the toolkits and the bike shelters.
PI's Background: Dr. Yertai Tanai
Project's date: December, 2024
Abstract: As an important economic hub and the fifth largest city in California, Fresno faces many challenges that one would not expect to encounter in the heart of the San Joaquin Valley, one of the most productive agricultural regions in the world. One of such challenge lies on Blackstone Avenue, an over eight-mile-long commercial corridor that connected the downtown core to the expanding suburbs. It has been known for crime, poverty, and vacant buildings that together speak of failed land use policy and lack of development ingenuity.
In a transformative move, in 2015, Fresno Area Express (FAX) embarked on a constructive journey by initiating the construction of a 15.7-mile Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) line known as the Q Line. The Q Line connects North Fresno, downtown Fresno, and Fresno's southeast growth area via Blackstone Avenue and Kings Canyon Road. The BRT service replaced existing local bus service in the corridor and offered decreased travel times through fewer stops and more frequent service. The project included transit signal priority, queue jump lanes, 27 stations, 17 low-floor compressed natural gas low-emission BRT vehicles, boarding platforms, fare machines, real time passenger information, and special branding to create a unique identity for the service. The Q Line began service in February 2018 and has since ridership surpassed 2.5 million passengers.In a transformative move, in 2015, Fresno Area Express (FAX) embarked on a constructive journey by initiating the construction of a 15.7-mile Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) line known as the Q Line. The Q Line connects North Fresno, downtown Fresno, and Fresno's southeast growth area via Blackstone Avenue and Kings Canyon Road. The BRT service replaced existing local bus service in the corridor and offered decreased travel times through fewer stops and more frequent service. The project included transit signal priority, queue jump lanes, 27 stations, 17 low-floor compressed natural gas low-emission BRT vehicles, boarding platforms, fare machines, real time passenger information, and special branding to create a unique identity for the service. The Q Line began service in February 2018 and has since ridership surpassed 2.5 million passengers.
PI's Background: Dr. Shahab Tayeb
Project's date: December, 2024
Abstract: The Internet of Vehicles (IoV) aims to facilitate the next generation of Connected and Autonomous Vehicles (CAV). In line with Objective 1 “Leverage new technologies, including vehicle automation, and innovative processes to achieve a seamless, multimodal surface transportation system that integrates with other “smart city” investments”, this project proposes the acquisition of hardware and software testbed for intra-vehicular networks. The adoption of Automotive Ethernet aligns with the objective of leveraging new technologies and innovative processes in the context of a seamless, multimodal surface transportation system integrated with smart city investments. It provides a technologically advanced and standardized communication framework that supports the goals of safety, efficiency, and connectivity within the evolving landscape of transportation and smart city initiatives.
Report Coming Soon
PI's Background: Dr. Fariborz M. Tehrani
Project's date: December, 2024
Abstract: This project aims to develop novel approaches to predicting and extending the concrete service life in pavement and bridge systems (Objective 2). Concrete materials provide durable solutions and contribute to the resilience of transportation infrastructure. However, the environmental footprints of cementitious contents raise concerns about their climate change impacts. Hence, enhancing the service life of concrete pavements and bridge decks is vital to reducing embodied energy and greenhouse gas emissions during the lifecycle of transportation systems (Objective 5). The project employs advanced techniques in service life prediction using transport properties of concrete (Objective 3). This project is aligned with Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) Every Day Count (EDC-7) Innovations, including Integrating GHG Assessment and Reduction Targets in Transportation Planning, Enhancing Performance with Internally Cured Concrete (EPIC2), and EPDs for Sustainable Project Delivery.
Year 6 (2023)
PI's Background: Dr. William H. Bommer, Dr. Emil Milevoj
Project's date: December, 2023
Research Objective:
1. What effect has the California seat belt law had on year-to-year seat restraint
usage rates of California drivers and
passengers?
2. What effect has the California seat belt law had on year-to-year seat restraint
usage rates of teen drivers and
passengers?
3. What effect has the California child restraint use law had on year-to-year restraint
usage rates for infants/children in
California?
4. What effect has California distracted driving law had on year-to-year distracted
driving rates of California drivers?
PI's Background: Dr. Yushin Ahn
Project's date: December, 2023
Abstract: Car-centric urban development patterns have given over vast swathes of land to multilane highways, congested arterials, and sprawling parking lots. These impervious surfaces are perceived as unsightly and alienating to many residents and have negative environmental impacts including the magnification of the urban heat island effect and reduction of downstream water quality. This research explores the use of various image classification methods on high resolution aerial imagery to quantify the percentage of urban areas covered by impervious surfaces. Traditional pixel- and object-based classification methods are compared to novel deep learning classification tools. The results are compared to past studies of impervious coverage in Fresno/Clovis and similar cities using other methodologies. Policymakers can use this information to inform future land use planning.
PI's Background: Dr. Jaymin Kwon
Project's date: December, 2023
Abstract: The main objective of the StarTraq 2023 project is to create safer communities and provide more significant opportunities for active transportation modes such as biking and walking, increasing access to transit. Through research on spatiotemporal analyses of roadside transportation-related air quality, everybody can enjoy the accessibility of transit and choices of healthier transit to improve their quality of life. The study aims to provide public information on transportation-related environmental exposure in a timely and relevant way so that people can use the knowledge for decision-making in designing and applying new materials and technologies to improve Californians’ public health. The proposed StarTraq project will further characterize the relationship of air quality between the federal reference monitoring data and local bike paths in the park and recreational areas, urban bike lanes for air quality, and on-road air quality by developing custom-built mobile air sensors.
PI's Background: Dr. Chihhao Wang
Project's date: December, 2023
Abstract: The objectives of this study encompass a diverse approach. This study aims to measure accessibility to urban opportunities, including jobs and services, while considering the influence of the Cal-High-Speed Rail (CHSR) within Fresno, Merced, and Kings. Furthermore, the research seeks to conduct a thorough pre- and post-implementation analysis of job and service accessibility within these three station cities at the census tract level. This study identifies regions where CHSR has the potential to enhance access to job and service opportunities within daily living spheres and areas where it would not. Ultimately, this research aims to provide transportation planning information for improving overall accessibility and promoting equal development through better connection to the local transpiration networks.
PI's Background: Dr. Hovannes Kulhandjian
Project's date: December, 2023
Abstract: In this study, we propose impersonating the work of the person helping students cross the street by developing a Digital Twin, a Smart Robot that allows pedestrians and cyclists to cross the street. It would detect the presence of a pedestrian and cyclist and the traffic flow using four different sensors appended onto it along with artificial intelligence. It would only cross the street and help the pedestrians/cyclists cross along. If it detects a danger during the crossing operation, it will alarm the driver and the pedestrians/cyclists. The intelligent robot technology we plan to develop can also be used for the second most vulnerable population, older people, to help them cross the street safely at a crossroads without traffic lights. The proposed system can be used both during the day and at night using a LIDAR, a thermal infrared camera, a radar system, and a video camera.
PI's Background: Dr. Christian Wandeler
Project's date: December, 2023
Abstract: This project aims to provide underserved minority students in afterschool programs opportunities to examine transportation careers and engage in community transformation through high-quality educational experiences. The project will build on the resources developed for the Central Valley Transportation Challenge and leverage the online transportation hub (funded by an SB 1 grant in 2020). The project will collaborate with afterschool program providers and connect them with CSU students, transportation, and engineering professionals from university and industry sectors to projects around transportation issues in the afterschool programs.
Objective:
- Transfer 100 lessons collected by the Fresno State Transportation Institute to an online platform, the online lesson plan hub, and make them accessible to after-school programs.
- Pilot the online lesson plan hub in after-school programs
- Develop five transportation lessons that can be self-managed by students
- Pilot the five self-managed lessons in after-school programs
PI's Background: Dr. Maria Calahorra-Jimenez
Project's date: December, 2023
Abstract: This research project aims to explore performance-based contracts (PBC) as a contracting strategy that might facilitate the application of new materials, design, and technology to address long-term road maintenance in California. This research contributes to objective 3 of the California Senate Bill (SB 1) by (1) identifying the benefits and limitations of PBC compared to traditional contracts and (2) exploring the experience of other states and countries in the implementation of PBC for road maintenance to inform the implementation of these types of contracts in California. This research project will contribute to the knowledge of project delivery and procurement methods by investigating the application of PBC to address long-term road maintenance in California. The results of this project will inform California road agencies in selecting the contracting strategy that best matches their long-term performance goals.
PI's Background: Dr. Manideep Tummalapudi
Project's date: December, 2023
Abstract: The objective aims to address Objective 2 of the California SB1 by identifying and developing tools and approaches that create cost-effective methods to improve the long-term benefits of transportation investments by developing innovative and cost-effective practical strategies to implement emerging inspection technologies for the construction and maintenance of bridges. California SB1 (Senate Bill) aims to “fix neighborhood streets, freeways, and bridges in communities across California” (State of California 2021). To accomplish this task, one of the essential activities is to inspect the condition of highway infrastructure, for which Caltrans spends almost 8% of its maintenance program budget (Caltrans report 2015-120). For example, Caltrans (California Department of Transportation) inspects and maintains 25,000 bridges in the state. Approximately 50% of these bridges have exceeded their design life, and it is essential to check them periodically. Accurate and timely bridge evaluations can help maintain a safe and reliable bridge network while optimizing the cost of repair activities, reducing the overall expenditure on bridges (Kim, Frangopol, & Soliman, 2013). Many emerging technologies, such as geospatial tools, 3D modeling, unmanned aerial systems (UASs), etc., have proved to be efficient in inspection of bridges. However, despite their potential to improve inspection quality and save inspection time and resources, the state DOTs have not yet fully implemented these emerging technologies for inspection activities, which costs all the state DOTs approximately $1.3 billion annually (Zulifqar, Cabieses, Mikhail, & Khan, 2014). Caltrans identified that effectively implementing UASs alone saved them $200,000 in 2021 (Caltrans Efficiency Report, 2020- 21), and being able to implement other technologies effectively would result in much higher savings. Therefore, it is essential through this research to identify emerging inspection technologies used for bridge highway inspection purposes, understand critical success factors for implementation, and develop approaches to implement these technologies effectively at the transportation agencies. In this way, this research supports the goals of SB-1 to improve the long-term benefits of transportation investments.
PI's Background: Dr. Shahab Tayeb
Project's date: December, 2023
Abstract: Blind intersections have high accident rates due to the poor visibility of oncoming traffic, high traffic speeds, and lack of road infrastructure (e.g., stoplights). These intersections are more commonplace in rural and suburban areas with underdeveloped traffic infrastructure. The Internet of Vehicles (IoV) aims to address such safety concerns through a network of connected and autonomous vehicles (CAVs) that intercommunicate. In line with Objective 1, “Leverage new technologies, including vehicle automation and innovative processes to achieve a seamless, multimodal surface transportation system that integrates with other “smart city” investments,” this project proposes a lightweight road-side unit (RSU) tailored to rural and suburban areas, aiming to minimize visibility issues by facilitating communications across such intersections. This is accomplished by creating an RSU based on Software Defined Radio (SDR) and Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) that utilizes an algorithm based on virtual traffic light methodologies. The components of the system will include an FPGA with an adaptive virtual traffic light algorithm, a communication module to monitor inter-vehicular communication, and a solar power system to optimize power usage. The implementation of the proposed system will reduce end-to-end delays. The main objectives of this proposal are threefold: (1) to study the impact of nonvisible communication on rural and suburban blind intersections; (2) to design a hardware implementation of an adaptive virtual traffic light that integrates into the existing IoV; and (3) to drive the reconfigurability of (2) using (1).

PI's Background: Dr. Jorge Pesantez
Project's date: December, 2023
Abstract: The main objective of this project is to develop a model to understand better the relationships between residents of the Central Valley area when an official agency sends out an evacuation alert in response to a wildfire threat. Based on developing a framework that evaluates novel information sources such as social media interactions among Central Valley's residents and official agencies, this project focuses on Objectives 1, 2, and 7 presented by the 2023 FSTI Call of Proposals. Our proposed model encompasses Objective 1 by leveraging novel information sources to evaluate the decision to evacuate or not. The proposal also covers RFP's Objective 2 about the long-term benefits of investments based on the evacuation routes that the project will evaluate considering wildfire threats. Finally, the most vital link between our proposal and RFP's Objective 7 relies on the model's ability to inform promptly about transportation-related issues focused on evacuation routes.
PI's Background: Dr. Yushin Ahn
Project's date:December, 2023
Abstract: Traffic sign detection is an essential task for transportation management. This task is usually done manually or semi-automatically using images captured by onboard cameras or LIDAR data obtained from airplanes, uncrewed aerial vehicles, or vans. This is very time-consuming and expensive. This process includes identifying objects on the road or in proximity. The previous works mainly focus on detecting and recognizing traffic signs based on onboard camera images. However, visual features of traffic signs, such as color, shape, and appearance, are often sensitive to illumination conditions, angle of view, etc. Besides the camera, LIDAR provides essential and alternative features for traffic signs. LIDAR is an active sensor that can capture a point cloud of XYZ points with intensity values. Intensity values correlate to the strength of the returned laser pulse, which depends on the reflectivity of the object and the wavelength used by the LIDAR. This characteristic can provide a critical alternative approach for capturing traffic signs; since signs are required to have reflective material for nighttime driving, we can use this property to our advantage when discriminating point clouds for signs. In most previous works, different colors of traffic signs are individually handled in a specific color space, which generally results in many thresholds or multiple classifiers. In this study, we use combined color spaces (CCS) to treat traffic sign colors as one class. For traffic sign recognition, regions of interest (ROIs) that suffer from perspective deformation are rectified first by fusing LIDAR and camera data to improve the robustness of any viewpoint variation. Then, the histogram of oriented gradient (HOG) features and linear support vector machines (SVMs) are used to classify traffic signs. Finally, extensive experimental results in challenging conditions show that our algorithm is robust and real-time. Our study compares information obtained from camera images and LiDAR measurements. This comparison is presented on three examples: traffic signs, road markings, and general pole-shaped things (e.g., city lights or trees). Further, we describe a process based on our algorithm that detects traffic signs in LiDAR measurement and transforms the results to a standard format used in geographic information systems. We tested our method on an approximately two-kilometer-long road in an urban area.
Year 5 (2022)
PI's Background: Dr. Aly Tawfik
Project's date: December, 2022
Abstract: Freight transportation represents a significant amount of traffic and all its associated externalities, such as traffic safety, congestion, energy demand, greenhouse, and air pollution emissions, and infrastructure costs. However, it also plays a primary role in the supply chains and the costs and availability of goods and is a major player of the economy. This study aims to identify, assess, and utilize different data sources to uncover and understand the patterns and movements of the different types of freight in different counties of the San Joaquin Valley. The San Joaquin Valley region consists of 8 counties naming San Joaquin, Stanislaus, Marced, Madera, Fresno, Kings, and Tulare. This research has explored some major datasets consisting of freight data such as GTA, PIERS, and Streetlight Data Insights for the year 2019, i.e., to get a clear insight on what the actual movement of freight looked like pre-covid. The primary softwares used for this analysis are MS Excel, MS Access, ArcGIS, and Jacob Streetlight Insight. This research investigated all modes of freight transportation for domestic and international trade which are air, water, rail, and road. Findings of this research are valuable for multiple different governments as well as private agencies for various use cases such as development of transportation infrastructure, freight business, and environment assessments.
PI's Background: Dr. Aly Tawfik
Project's date: May, 2022
Abstract: Over the past decades, different kinds of surveys have traditionally been the primary source of data for understanding travel demand (patterns and behaviors) in a region, and for developing the transportation planning models and designing the transportation infrastructure. However, the substantial evolution of communication technologies and the large market penetration of smartphones over the last decade have opened the door for novel types of data: cellphone trace big data. While traditional surveys will continue to provide value and answers that are not possible by cellphone trace big data, applications of this novel data source in transportation have been consistently growing and are expected to only grow further. This study utilizes cellphone trace big data (from Streetlight Data) to uncover the spatio-temporal distribution of travel demand (e.g. trips by mode) in the urban as well as rural areas in Fresno County, California. The study visualizes Origin-Destination (OD) patterns and OD trends by mode in the region and contrasts them with the existing transportation infrastructure. The study demonstrates the potential value of this novel data source as it provides additional and valuable information that can significantly improve our ability for understanding travel demand, and plan and design more efficient transportation systems to meet this travel demand.
Learning Objectives:
Articulate the advantages and limitations of travel surveys and cellphone trace big
data for transportation planning Discuss methods for using cellphone trace big data
to understand travel demand in urban and rural areas
Use cellphone trace big data to investigate the suitability of the existing transportation
infrastructure for serving its travel demand
Report Coming Soon
PI's Background: Dr. Aly Tawfik
Project's Start date: December, 2022
Abstract: The San Joaquin Valley (SJV) Electric Tractor Development & Demonstration project aims to analyze and demonstrate the potential benefits of utilizing the advanced technology of electric tractors and trucks in agricultural applications as an alternative to their diesel-powered counterparts. Fresno State Transportation Institute (FSTI) collaborated as the third-party data analyst with Project Clean Air, Humming Bird EV (HBEV), and Moonlight Companies to implement the SJV Electric Tractor Development & Demonstration for the California Air Resources Board (ARB) Off-Road Advanced Technology Demonstration Projects program. The contribution of FSTI in the project can be summarized in the following tasks: Providing a baseline report for current tractor fleet use and energy use at Moonlight Companies, Working directly with HBEV, the original equipment manufacturer, Moonlight Companies, the leading demonstration site, and other demonstration sites to collect necessary data for final analysis, Preparing a comprehensive plan for the collection of data in compliance with California ARB’s requirements, Designing data collection tools (i.e. surveys and logs) to collect and capture all required data, Assigning personnel to conduct field studies to observe use, operations, fueling process, and continuously efficiencies of the electric tractor versus the conventional fueled tractors, Working with Project Clean Air to provide data for quarterly and final reports.
Report Coming Soon
PI's Background: Dr. Aly Tawfik
Project's date: December 2022
Abstract: Traffic has a significant impact on public health. Traffic-related air pollution affects the health of individuals, especially when it comes to respiratory and cardiovascular health. A large number of people die due to respiratory and cardiovascular-related complications each year. According to the World Health Organization, 17.9 million people died because of cardiovascular diseases in 2016, representing 31% of all global death. Although the impact of the traffic- related air pollution on individuals is evident, the relationship between traffic-related air pollution and public health has been less investigated in the census tract level. The main goal of the study was to determine whether there was a relation between the health of a community, the traffic within them, and how they connect. Traffic and health data of the entire Fresno County were collected and then were analyzed at the census tract level. The results of this research showed a significant effect of traffic congestion on public health in the census tract level. The findings of this study could help in future planning and in the allocation of funds to help communities with health problems.
Report Coming Soon
PI's Background: Dr. Aly Tawfik
Project's date: May, 2022
Abstract: Traffic congestion is possibly one of the major negative impacts of travel. A large number of people are adversely affected by congestion each day in California and worldwide. In addition to global impacts such as greenhouse gas emissions and energy demand, traffic congestion significantly affects the direct population in areas where it occurs. It causes environmental degradation, significant loss of productive time, health impacts, and significant economic impacts. Measuring and identifying the causes of traffic congestion are necessary steps for understanding and reducing congestion. This study attempts to uncover some of the major causes of traffic congestion. The study analyzes traffic congestion in six major metropolitan areas in California: San Francisco and the Bay Area, Los Angeles, San Diego, Sacramento, Fresno and Bakersfield. The study investigated the possible impact of 35 different attributes on different measures of traffic congestion in these six metropolitan areas. Different attributes were acquired from a variety of data sources (e.g. road networks were collected from local Metropolitan Planning Organizations, MPOs). ArcGIS was utilized for most of the attribute computations. The 35 attributes are classified into 5 main groups: infrastructure attributes (e.g. roadway or lane miles normalized by population or area), connectivity attributes (e.g. roadway links or nodes normalized by area), socioeconomic attributes (e.g. median income and population density), weather attributes (e.g. days of precipitation), and trip attributes (e.g. number of carpools per household). Four different measures of traffic congestion were utilized: Travel Time Index, Roadway Congestion Index, Delay per Auto Commuter, and Cost per Auto Commuter. The results of this work indicated that the roadway miles per population and the number of roadway links per area were the two most highly and consistently significant variables in determining congestion. Roadway miles per population had a negative relationship with traffic congestion and the roadway links per area had a positive relationship. Results of this work could be helpful in understanding and addressing traffic congestion in urban areas.
Report Coming Soon
PI's Background: Dr. Hongwei Dong
Project's date: May, 2022
Abstract: The concept of smart transportation has received a lot of scholarly attention during the last decade. New mobility technologies and innovations, such as autonomous vehicles, electric cars, and shared mobilities, are revolutionizing the transportation industry and transforming American cities. To date, both the research and the implementation of smart transportation technologies have primarily focused on large urban and metropolitan areas. We have a limited understanding of the application and development of smart transportation technologies in small cities and rural areas. Can the promise of smart transportation be extended to small urban and rural communities? Will small urban and rural communities be left behind the smart transportation revolution? The objective of this study is to evaluate the development of smart transportation and smart city technologies in small urban and rural communities in California’s Central Valley, particularly those in Fresno County.
Specifically, this study attempts to achieve three goals. First, we survey the state-of-the-art practices of smart transportation technologies in both large and small cities as well as in rural communities in the United States. Second, we evaluate the development of smart transportation and smart city technologies in small urban and rural communities in California’s Central Valley by conducting surveys and interviews with local experts, transportation engineers, urban planners, and policy makers. The first-hand data collected through surveys and interviews are complemented by the second-hand data that are available from local planning agencies and other public data sources such as the U.S. Census Bureau. The first- and second-hand data allow us to evaluate the extent to which smart transportation has been implemented as well as the barriers to implementing smart transportation technologies in small urban and rural communities in the Central Valley. Lastly, we propose policy suggestions based on the successful experiences outside of the Central Valley and our careful evaluation of the development of smart transportation in small urban and rural communities in the Central Valley.
PI's Background: Dr. Hovannes Kulhandjian
Project's date: November, 2022
Executive Summary: There are over 590,000 bridges strewn across the network of highways stretching across the United States alone. The Federal Highway Act (FHWA) of 1968 mandates that each bridge with a length of 20 feet or more must be inspected at least once every 24 months. Each inspection must align with the criteria outlined by the National Bridge Inspection Standards (NBIS) [1]. Additionally, a bridge inspection will identify major structural issues that require follow-up, quantify the overall condition of the bridge to prioritize capital needs, identify routine maintenance, and catalog a history of the bridge’s condition. Inspecting bridges has been a labor-intensive and very costly process. Drones can potentially cut costs, provide better data, and improve worker safety during bridge inspections. Using drones for bridge inspections dramatically reduces the costs associated with the examination. This research proposes implementing an AI-based bridge and road inspection framework using drones with multiple sensor-collecting capabilities. It is not sufficient to do an inspection using cameras; we plan to utilize an infrared (IR) camera and a high-resolution optical camera. The IR camera can provide more details on the interior structural damages of a bridge than an optical camera, which is ideal for inspecting cracks on the surface of a bridge; in addition to that, our drone inspection system is equipped with a computer on-chip that runs Machine Learning algorithms that enable autonomous driving of the drone and taking images of the bridge or the road structure whenever it detects any damages. Instead of having a person operate the drone, it will self-operate and conduct the inspection process using the advanced AI algorithms we are developing.
PI's Background: Dr. Scott Peterson
Project's date: December, 2022
Abstract: Pavement performance investigation and evaluation is critical for pavement management systems (PMS) to maintain good driving conditions and prioritize maintenance or rehabilitation efforts and funding (Chun et al, 2021). For this purpose, agencies are interested in the type, extent, and severity of different distresses. The most important distresses include rutting, cracking (fatigue cracking and thermal cracking) for flexible pavement, and cracking and faulting for rigid pavement. There is specialized equipment available for the identification of pavement distresses and quantification of pavement condition. However, the specialized equipment generally has high variability, is subject to detection errors, and requires much labor, or costly efforts (Chun et al, 2021; Huang et al, 2014). Therefore, a reliable, accurate, time efficient, and cost‐effective way to collect pavement condition data and evaluate pavement performance is of interest. Recently, mobile phones and mobile electronic devices began adapting new camera and 3D sensing technologies. In 2020, the Apple iPad Pro and the Apple iPhone 12 Pro gained a new technology with a LiDAR sensor to help improve portrait mode photos in the day and night time. This new LiDAR sensor however has various not intended uses that need to be explored to identify further reaching capabilities that can be applied to many other applications, such as pavement performance.
PI's Background: Dr. Julio Roa
Project's date: December, 2022
Abstract: California is aggressively moving forward with efforts to deploy zero-emission transportation technology to fight climate change. However, to date, the investments California has made with Cap-and-Trade funding have focused on ground transportation and some marine sources. These sources are major contributors to climate change but do not represent the entirety of transportation modes in California. One mode of transport where California is lagging in recognizing the potential to reduce GHG emissions through electrification is air transport with the rapidly emerging development and deployment of zero-emission aircraft powered by battery/hybrid electric motors. There are over 140 public-use airports in California with 32 of those being in the San Joaquin Valley. Many of these airports are in close proximity to growing population and commerce centers, particularly in the San Joaquin Valley, but are underutilized. The development of advanced electric/hybrid electric is opening the door to using these airports for both passenger and freight movement through significantly reduced costs of operation associated with electric propulsion. Strategic investment in the supporting infrastructure to facilitate operations of these new aircraft in conjunction with zero- emission ground vehicles offers the potential to transform these existing airport assets into multi-modal, zero-emission transportation hubs for the communities they are located in; bringing enhanced mobility and increased economic activity to many communities currently isolated due to limited ground transportation connections. The objective of this project is to maximize opportunities for California’s cap-and-trade program to reduce the impact of greenhouse gas emission and transportation on climate change by comparing GHG emissions from both ground and air modes of transportation including evaluating new advances in air mobility being developed using electric/hybrid-electric propulsion for aircraft.
PI's Background: Dr. Fariborz Tehrani
Project's date: December, 2022
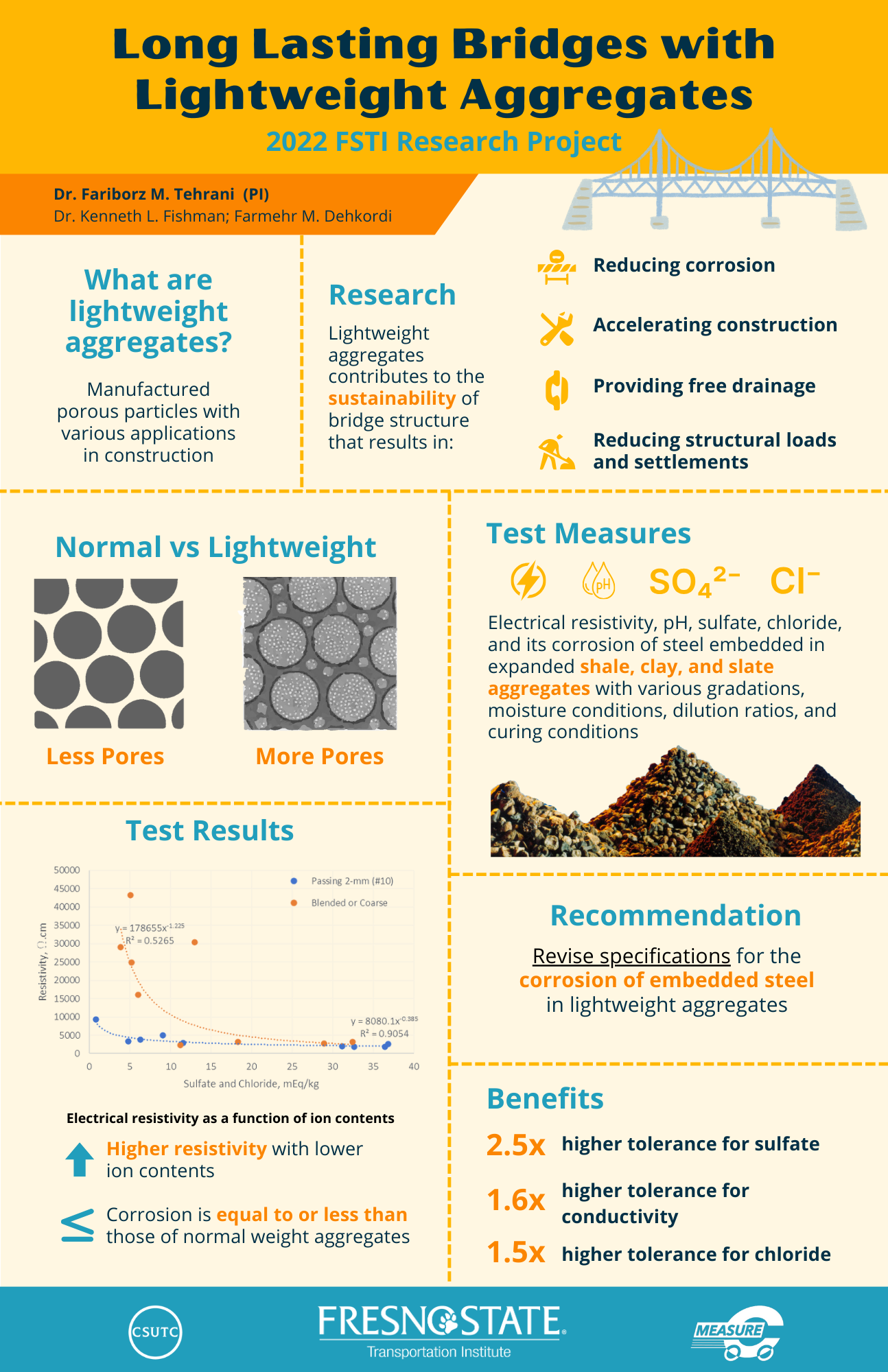
Abstract: The motivation for this research stems from the need for extending the service life, reducing the life cycle cost, and improving the safety and reliability of bridge abutments. This proposal endeavors to develop advanced solutions for application of rotary kiln manufactured lightweight aggregates in mechanically-stabilized earth (MSE) bridge abutments (Figure 1) to extend the service life of bridges and reduce the need for maintenance and rehabilitation of bridges, abutments, and approach and departure slabs on roadways. This solution identifies cost-effective MSE systems to delay or eliminate corrosion damages for long-term service life of roadways and bridges. The outcome of this proposal reduces the life-cycle cost, input energy, and greenhouse gas emissions associated with construction, maintenance, and rehabilitation of MSE bridge abutments and other backfills involving embedded steel products. The innovative approach of this proposal is the evolution of current testing methods to measure corrosion of reinforcing steel elelments as a function of electrochemical properties of backfill materials. This proposal extends and amends current national efforts led by the National Cooperative Highway Research Program (NCHRP), the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) and several Departments of Transporation (DOT) highlighting past achievements in Fresno State and new possibilities for the State of California.
PI's Background: Dr. Chih-Hao Wang
Project's date: December, 2022
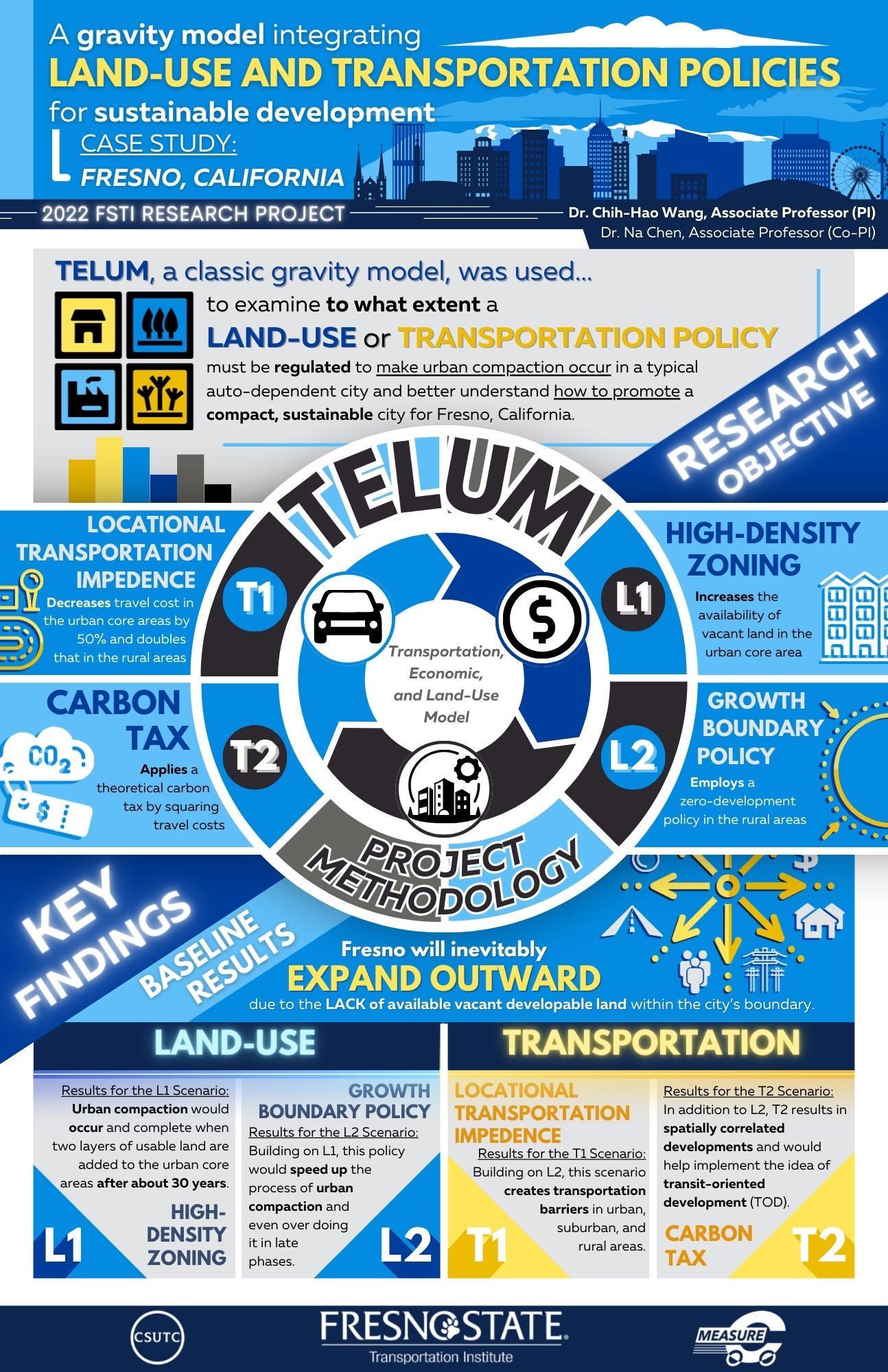
Abstract: Fresno, California is essentially the kind of a city that is continuously spreading out instead of building up with time. In the past decades, any of the locals can easily observe that the city has been spreading out to the north (e.g., those in the north from the Copper Ave) and east (e.g., those in the southeast from the Fowler Ave). The above-mentioned edge cities can be even found along Highway 41 toward Madera County, such as the new built Tesoro Viejo neighborhood, although there are some renewed apartments with a higher density structure found in the downtown area. To help Fresno move toward sustainability requires the understanding of the effects of varied transportation investments and land-use restrictions, such as the provision of public transit and bike lanes, high density zoning, and growth boundary. However, this had not been done in the past to provide a research framework to comprehensively evaluate either such a transportation or land-use policy for the promotion of a compact city toward sustainability, and therefore is needed.
PI's Background: Dr. Jaymin Kwon
Project's date: December, 2022
Abstract: The San Joaquin Valley (SJV) has been known for poor air quality and high rates of respiratory-related illnesses. Veloz et al. (2020) conducted a study on perceptions about air quality in SJV residents and found that a majority of the participants are worried about air quality. Hence, promoting alternative forms of transportation is critical in our community. In this research, we propose to examine the baseline air pollution exposure of pedestrians, cyclists, drivers, and passengers during transportation. This study will provide valuable findings that are useful for planning transportation facilities more efficiently to protect people, promoting active transportation modes, and increasing awareness of clean air efforts in transportation for healthier communities.
Year 4 (2021)
PI's Background: Dr. Jaymin Kwon
Project's date: December, 2021
Abstract: Promoting alternative forms of transportation is a major focus area in Transportation Planning. Information on pedestrians' and cyclists' exposure to traffic-related air pollutants during commute and utilization of parks and recreational areas is very limited in our Fresno/Clovis area. This proposed research will provide valuable insights and findings that could be used to plan transportation facilities better and promote more active transportation. The purpose of our proposal is to continue and expand the StarTraq 2020 project that is currently funded by the Fresno State Transportation Institute (FSTI) to meet the identified needs of the Fresno/Clovis area, promoting alternative forms of transportation by examining air pollution data collected near roadways and on trails as related to the active transportation modes of walking and bicycling. Through this research, we attempt to broaden the scope of the roadside, on-road, and in-vehicle air quality data from particle pollutants.
Objective: This research attempts to broaden the scope of the roadside, on-road, and in-vehicle air quality data from particle pollutants. The results will provide the baseline exposure levels for public health concerns of different transportation modes. In addition, the information on pedestrians' and cyclists' exposure to traffic-related air pollutants during commute and utilization of parks and recreational areas will be precious to promote the active transportation mode while developing strategies for reducing the risks associated with the mode of transportation via urban planning and policy development.
PI's Background: Dr. Chihhao Wang
Project's date: December, 2021
Abstract: One motivation of widely studying accessibility is that the transportation network of a city influences individuals’ mobility and therefore affects their daily activities. Despite all these, it is rare to assess its resilience considering the increasingly and frequently emergent natural hazards. This study aims to fill out this gap by developing an analytical research framework to examine the resilience of accessibility to emergency and lifesaving facilities under the threats of natural hazards such as earthquakes and wildfires. The results reveal whether the existing transportation network is resilient to potential impacts from natural disasters and point out the most vulnerable areas in terms of emergency accessibility. The findings will provide a new insight into the accessibility-based planning of promoting a safe and resilient city. With the widely used cumulative-opportunity approach, we measure accessibility by counting emergency and lifesaving facilities (including parks, schools, hospitals, roads, and fire stations) that can be reached by driving at the census tract level in San Fernando Valley, CA. With the calculated accessibility, certain simulations are conducted to collect a set of pseudo data for what would happen if an arbitrary road were damaged by a selected disaster. To check this impact, the above-mentioned approach is used to recalculate accessibility by taking out a street segment located in hazardous areas from the transportation network system, one at a time, until the number of simulations is large enough for statistical analysis. With the results, accessibility damage hotspots are identified to point out the most vulnerable locations and statistical analysis is used to identify those areas where accessibility is significantly reduced compared to the original status. A normalized difference accessibility index (NDAI) is further created to suggest plans and strategies to help those vulnerable areas through adding facilities/services or improving transportation infrastructure.

PI's Background: Dr. Hovannes Kulhandjian
Project's date: December, 2021
Abstract: The goal of this research work is to maximize the detection capabilities of pedestrians, especially at night, by effectively data fusing the information gathered from a thermal camera, a radar sensor and a video camera along with the use of advanced machine learning algorithms to detect and avoid pedestrian collision in real-time. Using this multi- dimensional valuable data, it could make intelligent decisions during different conditions of the road, be it during the day or at night. The proposed system could potentially be imbedded into a smart car system that provides real-time pedestrian detection and alerting mechanism by vibrating the driver’s wheel and display a message on a monitor/dashboard to warn the driver to avoid colliding into the pedestrian. The proposed system can be used both during the day and at night using the combination of thermal infrared camera, a radar system and a video camera. It could also be installed in an autonomous vehicle. The PI has research expertise in the area of sensing combined with Artificial Intelligence. His most recent FSTI research work was based on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. Recently, he presented two conference papers, please refer to [11, 12] one was in a flagship Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) held in Hawaii while the other was in an International Conference run by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) held in Atlanta, Georgia
Objective: One possible solution is to use a video camera, a radar system, or a LIDAR system in a vehicle. More recently, the advancement of thermal IR cameras has shown a potential possible solution. The research on pedestrian detection and avoidance is still in its infancy. Several methods have been explored to detect a pedestrian and avoid an accident. To the best of our knowledge, no prior research work has explored or experimented with the idea of using Data Fusion from multiple sensors (i.e., a thermal infrared camera, radar sensor, and a visible camera) combined with advanced Machine Learning (ML) for pedestrian detection and avoiding mechanize. Therefore, we believe that this research exploration could lead to new Artificial Intelligent-based application tools for drivers that could potentially save lives. We will be exploring state-of-the-art ML techniques combined with data fusion to achieve this objective. The goal of this research work is to maximize the detection capabilities of pedestrians, especially at night, by effectively data fusing the information gathered from a thermal camera, a radar sensor, and a video camera along with the use of advanced machine learning algorithms to detect and avoid pedestrian collision in real-time. Using this multi-dimensional valuable data, it could make intelligent decisions during different conditions of the road, be it during the day or at night. The proposed system could potentially be embedded into a smart vehicle system that provides real-time pedestrian detection and alerting mechanism by vibrating the driver’s wheel and display a message on a monitor/dashboard to warn the driver to avoid colliding into the pedestrian. The proposed system can be used both during the day and at night using the combination of a thermal infrared camera, a radar system, and a video camera. It could also be installed in an autonomous vehicle.
PI's Background: Dr. Shahab Tayeb
Project's date: December, 2021
Abstract: This study analyzes the security of a common in-vehicle network standard, the Controller Area Network (CAN). Due to its inherent vulnerabilities to various forms of cyber-attacks, CAN implementations can easily be targeted by cybercriminals. Such vulnerabilities range from eavesdropping, where the attacker can read the raw data traversing the vehicle, to spoofing, where the attacker can place fabricated traffic on the network. We, initially, perform a simulation of CAN traffic generation followed by hardware implementation of the same on a test vehicle. Due to the obscure nature of CAN, we reverse-engineered the missing parameters through a series of passive sniffing attacks on the network. Finally, we demonstrate the feasibility of the attack by placing fabricated frames on the CAN.
PI's Background: Dr. Julio Roa
Project's Start date: December, 2021
Project's End date: May, 2022
Executive Summary: The objective of this project [A1] seeks to determine how Regional Air Mobility (RAM)
using electric/hybrid electric aircraft can provide new high-speed transportation
for high priority passenger and cargo movement within Fresno County and connections
to coastal urban centers. It is achieved by researching the demand for regional air
travel generating an inventory of existing infrastructure, studying new technology
available, studying infrastructure requirements from the landside and the airside,
and evaluating the potential for integration with, and enhancement of, current and
planned ground transportation services.
Regional Air Mobility (RAM) using electric aircraft will become a reality within the
next 10 years and transform both air and ground transportation by offering a new service
using existing, underutilized airports that will change them into vibrant hubs for
zero emission transportation for the communities they serve. Using small 5-20 passenger
all electric or electric-hybrid aircraft, RAM services will provide connectivity for
both passengers and freight to communities where ground transportation currently provides
the bulk for goods and people movement.
The San Joaquin Valley is an area of California that could benefit greatly from RAM
services due to the large land area of the region, the presence of over 30 general
use airports from Bakersfield to Stockton, and the need for improved connectivity
for communities within the region with the urban centers in the north and south. In
spite of having many small airports near cities in the region, there is currently
only limited commercial air service available, leaving most of the region reliant
on ground transportation. Understanding the potential of RAM to become an economic
engine for communities with these underutilized airport assets was an important outcome
for this research.
Project Objective and Motivation: Advances in electric aircraft development are providing opportunities for new Regional
Air Mobility services that can enhance connectivity of regions by using underutilized
existing airport infrastructure and integrating use of electrified ground transportation.
This research project seeks to determine how RAM using electric/hybrid electric aircraft
can provide new high-speed transportation for high priority passenger and cargo movement
within Fresno County and connections to coastal urban centers. This project also seeks
to study the potential opportunities and challenges to effectively implement (electric/hybrid)
RAM in the San Joaquin Valley.
This study covers a range of topics to help clarify what RAM is and why it matters.
It should not be construed as the final, defining source of all knowledge when it
comes to possibilities and best ways forward as they relate to RAM initiatives. Rather,
this study is intended to start a conversation with the communities that will be participants
in what is an evolving RAM deployment process.
The focus of this study is what is needed in terms of RAM development in order to
effectively implement RAM for high-priority cargo and passengers.
PI's Background: Dr. Maria Calahorra-Jimenez
Project's Start date: December, 2021
Project's End date: July, 2022
Abstract: Improving long-term performance in highway projects is an imperative goal for public administrations. Project delivery and procurement methods might provide an opportunity to align design and construction processes with this goal. Previous studies have explored whether project delivery methods impact the long-term performance of highway projects. However, these studies did not focus specifically on how core elements within the procurement might relate to long-term performance. Thus, this research aims to fill this gap by exploring to what extent and how long-term evaluation criteria are considered in design-build best-value procurement of highway projects. To this end, content analysis was conducted on 100 projects procured between 2009 and 2019 by 19 DOTs across the U.S. The analysis of 365 evaluation criteria found that (1) roughly 11% of them related to long-term performance. (2) The weight given to these criteria in the overall technical proposal was lower than 30%. (3) Sixty-five percent (65%) of long-term evaluation criteria focused on design while 15% related to materials and technology, respectively. The results of this study are a first steppingstone to initiate a deep exploration of the relationship between procurement practices and actual project performance. Currently, with sustainability and life cycle assessments being top concerns in infrastructure projects, this line of research might be of particular interest to DOTs and highway agencies across the U.S. and worldwide.
Objective: In this research, the objective of the content analysis is twofold. First, it aims to identify to what extent RFPs include long-term performance evaluation criteria. To this end, the researcher used quantitative content analysis. Second, the study seeks to explore how long-term goals and evaluation criteria relate to various assessment categories. To this end, the researchers conducted a qualitative content analysis.
Year 3 (2020)
PI's Background: Dr. Chih-Hao Wang
Project's Start date: March 1 2020
Project's End date: Dec 3 2020
Executive Summary:
Objectives:
- Explore the explicit local relationships between cycling activities (utilitarian and/or recreational) and the accessibility to multi-use paths through cycling computed from the previous CSUCT SB1 project for Fresno in California, using a geographically weighted (GWR) regression model;
- Provide planning information for active transportation strategies for Fresno, California;
- Present the analysis results in a planning conference, such as the Association of Collegiate Schools of Planning (ACSP) annual meeting.
Motivation:
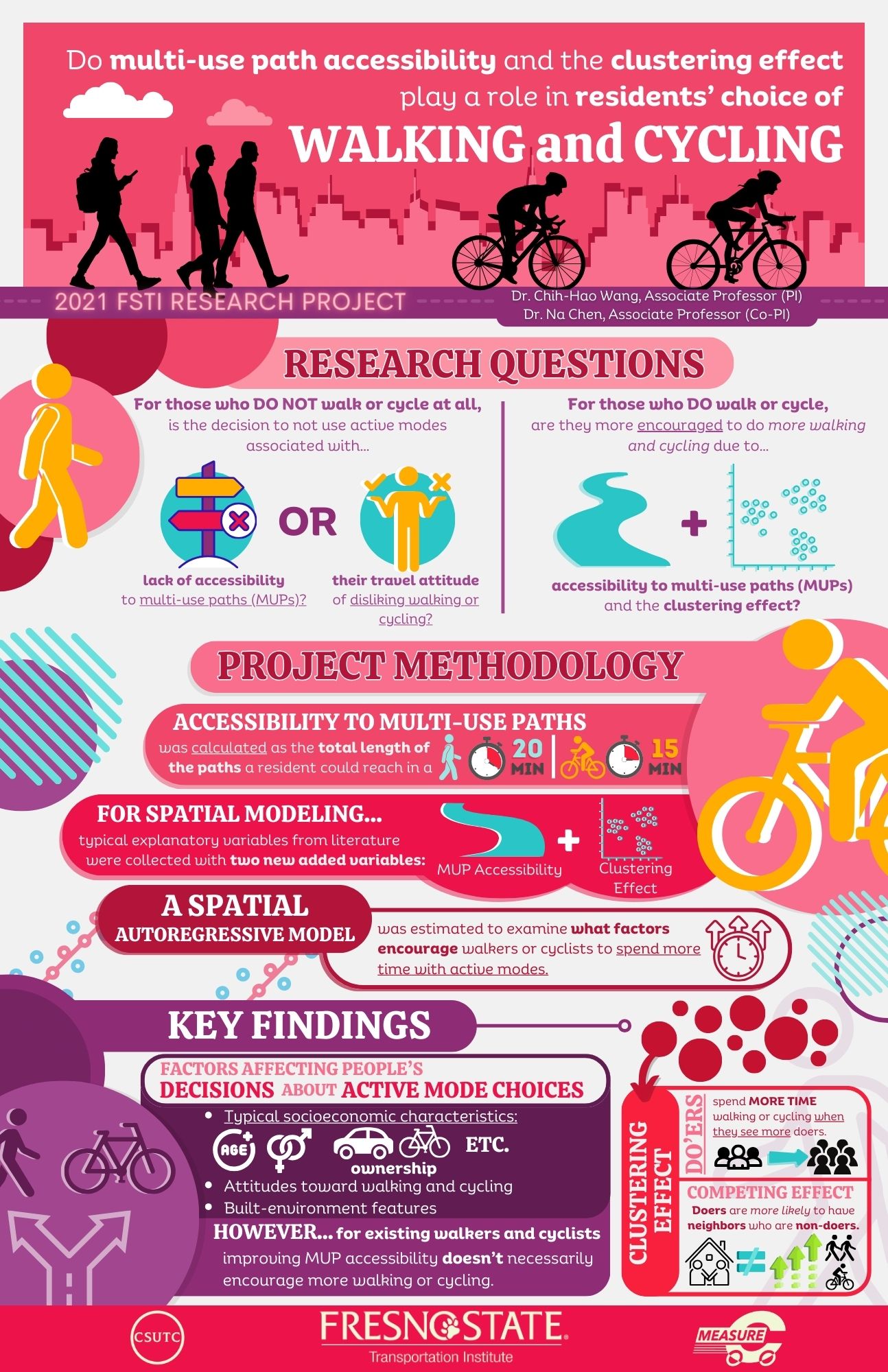
This research proposal is an extension of the two previous SB1 projects that (1) one calculated the accessibility to multi-use paths through cycling using the network analysis in the ArcGIS, and (2) the other found an optimal allocation of transportation investments that would maximize the total accessibility to multi-use paths through cycling while minimizing the gap between high- and low-accessibility neighborhoods. Along this line, it is interesting to explore whether the accessibility to multi-use paths would affect residents’ cycling activities, especially for those from socioeconomic disadvantaged neighborhoods. Therefore, this proposed project is designed to serve this purpose using a GWR model to examine the local relationships between the intensity/frequency of cycling activities and the effects of accessibility to multi-use paths through cycling while controlling for other built environment and social demographical factors. The results will point out where the accessibility does not work and therefore some other policy interventions might be needed to promote cycling activities. In other words, this study aims at revealing whether the residents who do not cycle is because of the lack of accessibility or their cycling perception or behavior. The findings will provide a new insight into the planning problem of promoting active transportation for Fresno, California.
Project's Start date: Feb 1 2020
Project's End date: Dec 31 2020
Executive Summary:
The goal of the Fresno State Transportation Challenge is to create an authentic civic service-learning experience, in which K-12 students and teachers; university students and professors; and community members work together on projects addressing transportation concerns and related issues in the region. During 2019 we piloted the Transportation Challenge process with 9 teachers. In 2020 the goal is to expand, refine, and create structures to sustain the implementation of the Transportation Challenge across subsequent years.
The objectives to meet this goal are as follows: 1) Conduct research on the implementation and expansion of the Transportation Challenge program to identify content and procedural supports and challenges; 2) Develop a pipeline for recruitment and continuous participation of K-8 teachers across the Central Valley; 3) Convene participating teachers and FSTI members to analyze instructional procedures and materials to develop a Transportation Challenge curriculum; and 4) Develop structures for increasing the connections between local educators and FSTI members and resources.
PI's Background: Dr. Jaymin Kwon
Project's Start date: March 1 2020
Project's End date: Dec 31 2020
Abstract: To promote active transportation modes (such as bike ride and walking), and to create safer communities for easier access to transit, it is essential to provide consolidated data-driven transportation information to the public. The relevant and timely information from data facilitates the improvement of decision-making processes for the establishment of public policy and urban planning for sustainable growth, and for promoting public health in the region. For the characterization of the spatial variation of transportation-emitted air pollution in the Fresno/Clovis neighborhood in California, various species of particulate matters emitted from traffic sources were measured using real-time monitors and GPS loggers at over 100 neighborhood walking routes within 58 census tracts from the previous research, Children’s Health to Air Pollution Study - San Joaquin Valley (CHAPS-SJV). Roadside air pollution data show that PM2.5, black carbon, and PAHs were significantly elevated in the neighborhood walking air samples compared to indoor air or the ambient monitoring station in the Central Fresno area due to the immediate source proximity. The simultaneous parallel measurements in two neighborhoods which are distinctively different areas (High diesel High poverty vs. Low diesel Low poverty) showed that the higher pollution levels were observed when more frequent vehicular activities were occurring around the neighborhoods. Elevated PM2.5 concentrations near the roadways were evident with a high volume of traffic and in regions with more unpaved areas. Neighborhood walking air samples were influenced by immediate roadway traffic conditions, such as encounters with diesel trucks, approaching in close proximity to freeways and/or busy roadways, passing cigarette smokers, and gardening activity. The elevated black carbon concentrations occur near the highway corridors and regions with high diesel traffic and high industry.
PI's Background: Dr. Samer Sarofim
Project's Start date: March 1, 2020
Project's End date: December 31, 2020
Abstract: This research empirically investigates the need for, and the effective design and content of, a proposed mobile application that is targeted at pedestrians and cyclists in Fresno County. The differential effect of the proposed mobile app name and colors on the target audience opinions was examined. Further, app content and features were evaluated for importance and the likelihood of use. This included design appeal, attractiveness, relevance, ease of navigation, usefulness of functions, personalization and customization, message recipients’ attitudes towards message framing, and intended behaviors related to pedestrian, cyclist, and motorist traffic safety practices. Design mobile application features tested included image aesthetics, coherence and organization, and memorability and distinction. Potential engagement with the mobile app was assessed via measuring the users’ perceived enjoyment while using the app. The behavioral intentions to adopt the app and likelihood to recommend the app were assessed. The willingness to pay for purchasing the app was measured. This research provided evidence that a mobile application designed for pedestrians and cyclists is needed, with high intentions for its adoption. Functions, such as Safety Information, Weather Conditions, Guide to Trails, Events for Walkers and Bikers, and Promotional Offers are deemed important by the target population. This research was conducted in an effort to increase active transportation mode utilization and to enhance the safety of vulnerable road users. The public, city administrators, transportation authorities, and policy makers shall benefit from the results of this study by adapting the design and the features that are proposed in this research and were found appealing and useful for the target vulnerable road user groups. The need of the proposed mobile application and its main functions are established, based on the results of this research, which propagates further steps of implementation by city administrators and transportation authorities.
PI's Background: Dr. John Green
Project's Start date: May 1, 2020
Project's End date: December 31, 2020
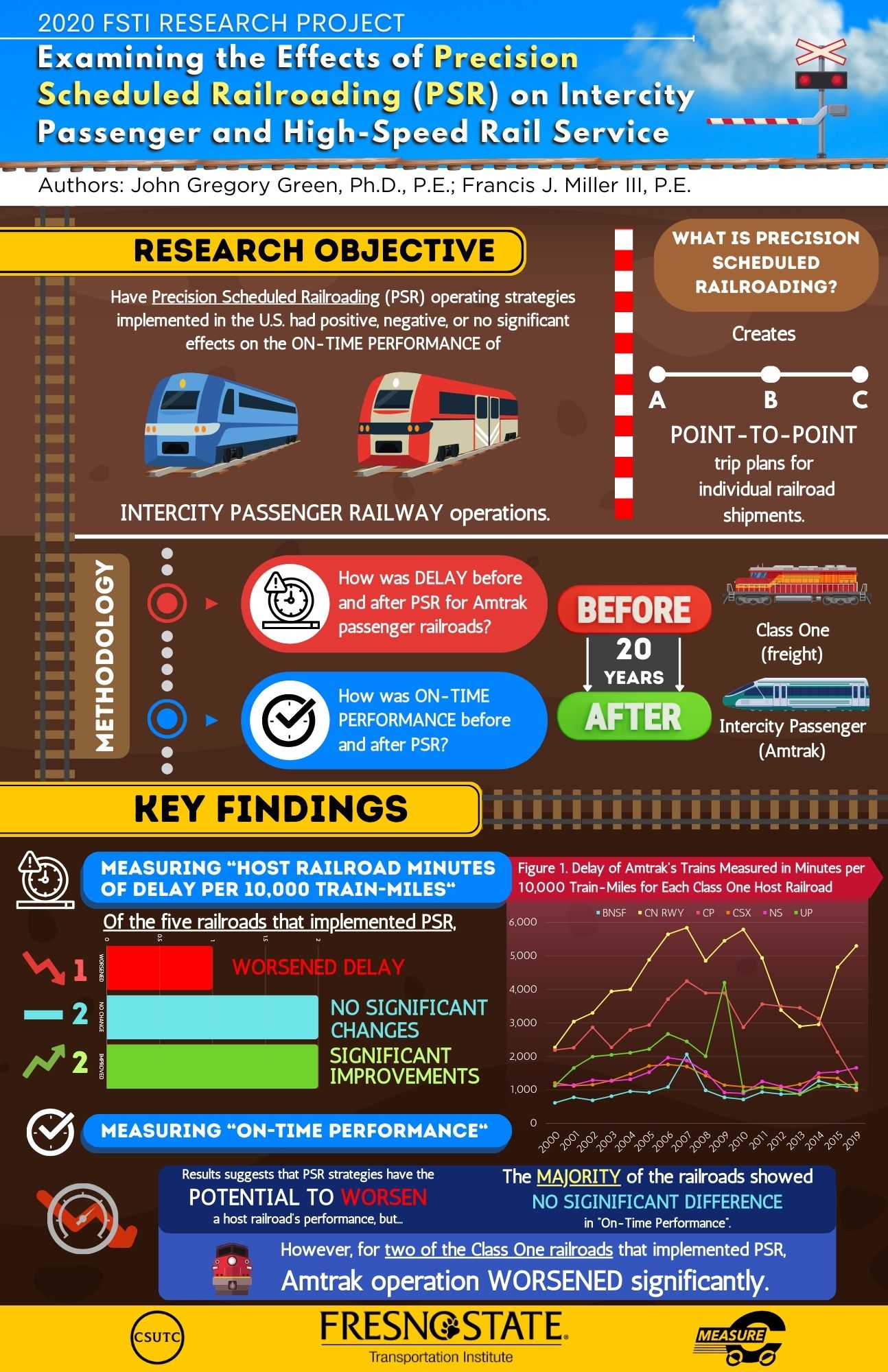
Abstract: More than just scheduling terminal-to-terminal trips for trains, “Precision Scheduled Railroading” (PSR) creates entire point-to-point trip plans for individual railroad shipments. Since precision execution was first put into practice, the benefits to shipment arrival reliability and to freight railroads’ profitability have been demonstrated by its use in several Class One freight railroads. However, the effects of the PSR operating strategy on passenger railway operations in shared freight/passenger corridors has not been studied in detail. This research examines the effects of PSR railroad operations on passenger railways, including measuring “Host Railroad Minutes of Delay per 10,000 Train-Miles” and “On-Time Performance” of individual passenger railways, both intercity and high-speed.

PI's Background: Dr Hovannes Kulhandjian.
Project's Start date: 03 June, 20120
Project's End date: December 31, 2020
Abstract: According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, in 2017 drowsy driving resulted in 50,000 injuries across 91,000 police-reported accidents, as well as almost 800 deaths. Through the application of visual and radar sensors combined with machine learning, this research developed a drowsy driver detection system aimed to prevent potentially fatal accidents. The working prototype of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems can be installed in present- day vehicles to detect drowsy drivers with over 95% accuracy. It integrates two types of visual surveillance to examine the driver for signs of drowsiness. A camera is used to monitor the driver’s eyes, mouth and head movement in order to recognize when a discrepancy occurs in the driver's eye blinking pattern, yawning incidence, and/or head drop, thereby signaling that the driver may be experiencing fatigue or drowsiness. The micro-Doppler sensor in the system allows the driver's head movement to be captured at all times. Through data fusion and deep learning, the system quickly analyzes and classifies a driver's behavior under various conditions in real-time monitoring. This research could be implemented to reduce drowsy driving, thereby, making the roads safer for everyone and ultimately saving lives.
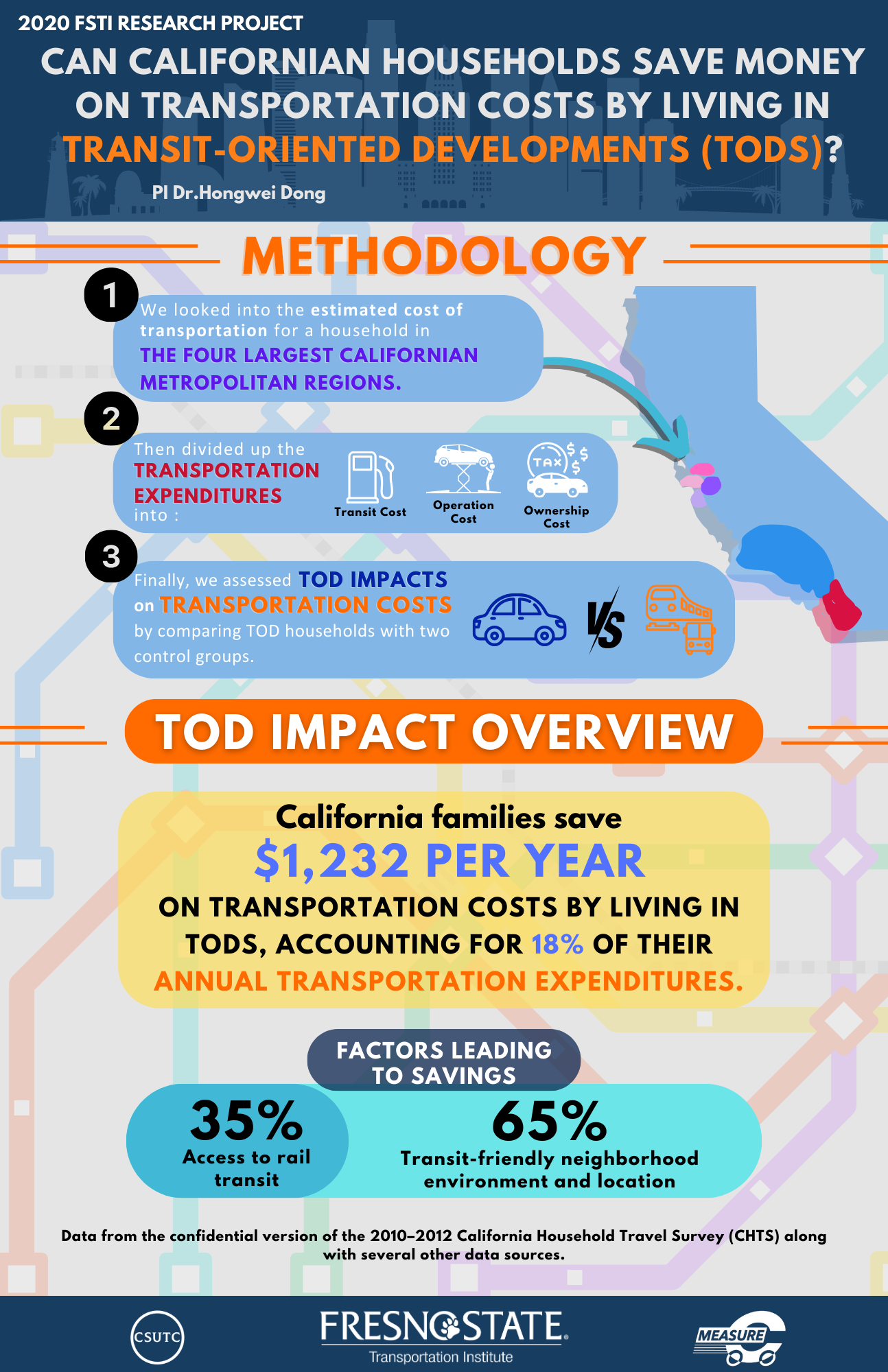
PI's Background: Dr. Hongwei Dong
Project's Start date: April 1, 2020
Project's End date: December 31, 2020
Abstract: Many residents in large Californian metropolitan areas are heavily burdened by housing costs. Advocates, researchers, and elected officials in California are debating whether transit-oriented development (TOD) could be an effective tool to mitigate the housing affordability problem by increasing housing supply and reducing transportation costs in transit-rich neighborhoods. This study contributes to this debate by estimating how much Californian families can save on transportation costs by living in transit-oriented developments (TODs). By utilizing the confidential version of the 2010– 2012 California Household Travel Survey, this study evaluates the impact of TOD on household transportation expenditures by comparing TOD households with two control groups. When controlling for household demographics, TOD households save $1,232 per year on transportation expenditures—18% of their total annual transportation expenditures. When controlling for both demographics and neighborhood environment, TOD households save $429 per year—about 6% of their total annual transportation expenditures. The study confirms that Californian households save money on transportation costs by living in TODs, mainly because they own fewer vehicles. About two-thirds of the savings can be attributed to a transit-friendly neighborhood environment and one-third to access to rail transit, which highlights the importance of integrating a rail transit system with supportive land use planning and neighborhood design.
PI's Background: Dr. Shahab Tayeb
Project's Start date: March 1, 2020
Project's End date: December 31, 2020
Abstract: As an emerging field, the Internet of Vehicles (IoV) has a myriad of security vulnerabilities that must be addressed to protect system integrity. To stay ahead of novel attacks, cybersecurity professionals are developing new software and systems using machine learning techniques. Neural network architectures improve such systems, including Intrusion Detection System (IDSs), by implementing anomaly detection, which differentiates benign data packets from malicious ones. For an IDS to best predict anomalies, the model is trained on data that is typically pre-processed through normalization and feature selection/reduction. These pre-processing techniques play an important role in training a neural network to optimize its performance. This research studies the impact of applying normalization techniques as a pre-processing step to learning, as used by the IDSs. The impacts of pre-processing techniques play an important role in training neural networks to optimize its performance. This report proposes a Deep Neural Network (DNN) model with two hidden layers for IDS architecture and compares two commonly used normalization pre-processing techniques. Our findings are evaluated using accuracy, Area Under Curve (AUC), Receiver Operator Characteristic (ROC), F-1 Score, and loss. The experimentations demonstrate that Z-Score outperforms normalization and the use of Min-Max normalization.
PI's Background: Dr. Aly Tawfik
Project's Start date: December, 2020
Project's End date: June, 2022
Executive Summary and Objective: COVID-19 may have forever changed our world. Given the limited space and air circulation, potential infections on public transportation could be concerningly high. Accordingly, this study has two objectives: (1) to understand air circulation patterns inside the cabins of busses; and (2) to test the impact of different technologies in mitigating viruses from the air and on surfaces inside bus cabins. For the first objective, different devices, metrics and experiments (including colored smoke; videotaping; anemometers; pressure differentials; particle counts; and 3D numerical simulation models) were utilized and implemented to understand and quantify air circulation inside different busses, with different characteristics, and under different operating conditions (e.g. with windows open and shut). For the second objective, three different live prokaryotic viruses were utilized: Phi6, MS2 and T7. Various technologies (including positive pressure environment inside the cabin, HEPA filters with different MERV ratings, concentrated UV exposure with charged carbon filters in the HVAC systems, center point photocatalytic oxidation technology, ionization, and surface antiviral agents) were tested to evaluate the potential of mitigating COVID-19 infections via air and surfaces in public transportation. The effectiveness of these technologies on the three live viruses was tested in both the lab and in buses in the field. The results of the first objective experiments indicated the efficiency of HVAC system designs, where the speed of air spread was consistently much faster than the speed of air clearing. Hence, indicating the need for additional virus mitigation from the cabin. Results of the second objective experiments indicated that photocatalytic oxidation inserts and UVC lights were the most efficient in mitigating viruses from the air. On the other hand, positive pressure mitigated all viruses from surfaces; however, copper foil tape and fabrics with a high percentage of copper mitigated only the Phi6 virus from surfaces. High- temperature heating was also found to be highly effective in mitigating the different viruses from the vehicle cabin. Finally, limited exploratory experiments to test possible toxic by-products of photocatalytic oxidation and UVC lights inside the bus cabin did not detect any increase in levels of formaldehyde, ozone, or volatile organic compounds. Implementation of these findings in transit buses, in addition to the use of personal protective equipment, could be significantly valuable for protection of passengers and drivers on public transportation modes, possibly against all forms of air-borne viruses.
PI's Background: Dr. Christian Wandeler
Project's date: December, 2020
Abstract: The Fresno State Transportation Challenge uses an action civics approach to support K-12 students in developing transportation-related projects that have a positive impact on the community. In 2020 the goal was to expand, refine, and create structures to sustain the implementation of the Transportation Challenge across subsequent years. As a result of the COVID pandemic, the process and goals of the project were adapted. The project was extended into April 2021 and was entirely conducted through remote participation. The focus was on two high schools. The expansion into the high school age bracket was successful and the experience with these two projects will allow for easier expansion in additional high schools in the future. One high school focused on the topic of active mobility, specifically biking, and addressed the challenge of how to get more students to bike to school. The other high school combined the transportation challenge with an economic vitalization project. The students were asked to also develop a modern transportation concept. Both projects exposed high school students to the topic of transportation and expanded awareness of transportation careers. Students also developed important competencies in the domains of problem solving, collaboration, communication, and leadership.
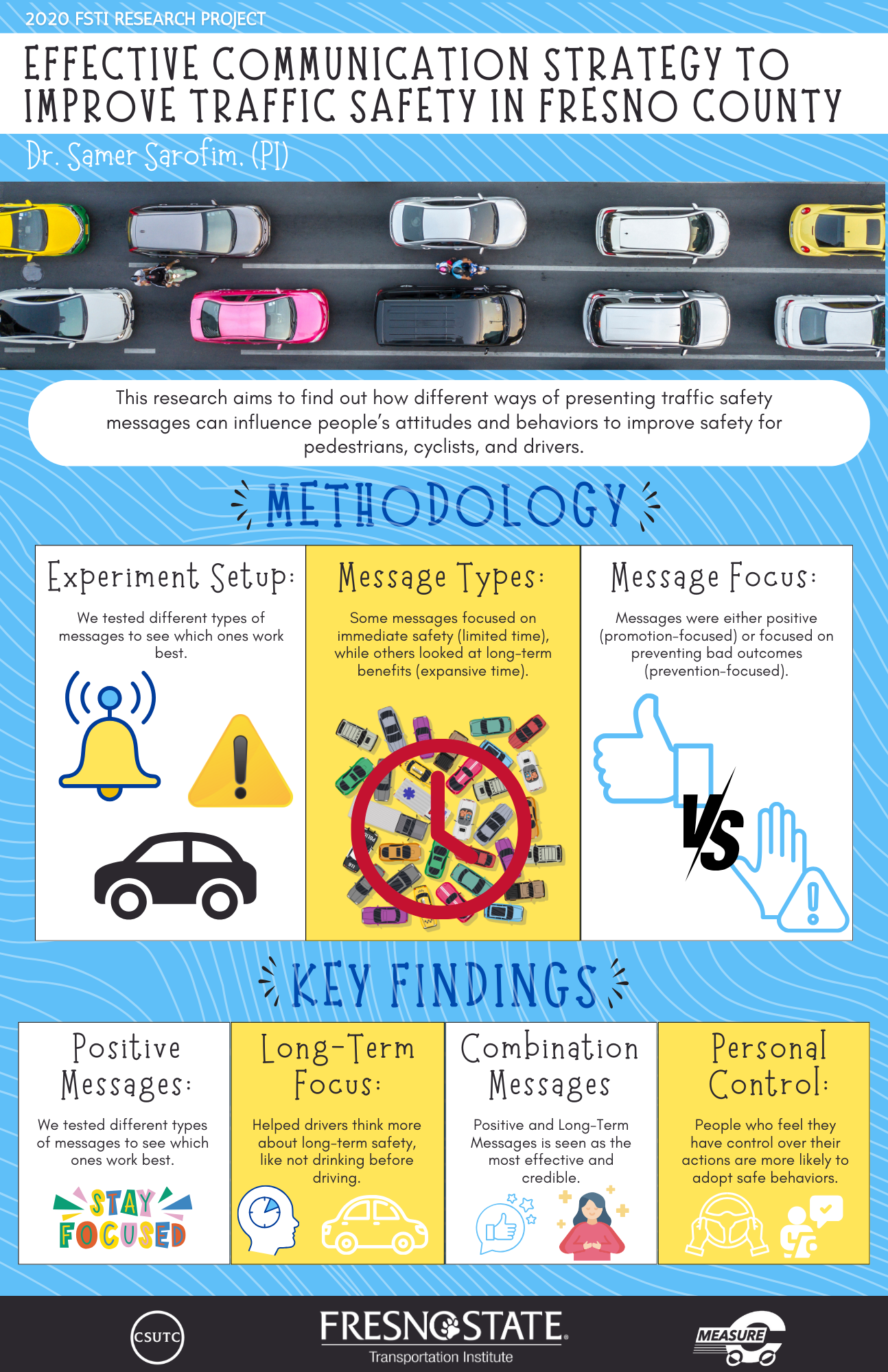
PI's Background: Dr. Samer Sarofim
Project's published date: June, 2020
Abstract: This research empirically investigated the differential effect of message framing on message recipients’ attitudes and intended behaviors related to pedestrian, cyclist, and motorist traffic safety practices. The framework empirically investigated time horizon (expansive vs. limited) and regulatory focus (prevention vs. promotion) message framing. The time horizon in the message can make someone either think of the future (expansive) or the present (limited). For example, an expansive time horizon message communicates that life is long and directs the focus on the future. On the contrary, a limited time horizon message communicates that life is short and directs the focus on the present moment. The regulatory focus of the message can direct the message recipients’ attention to take certain action to either avoid negative consequences (prevention) or attain positive outcomes (promotion). The research examined the role of the individual difference of perceived personal control on the perceptions of the presented messages and behavioral intentions to adopt safe transportation practices. Various messages were designed to employ a multilayer framing and fit with a 2 (time horizon: expansive vs. limited) x 2 (regulatory focus: promotion vs. prevention) between- subjects design. Findings suggest the messages adopting the expansive and promotion-focused framing combination seem to be more effective and have a higher tendency to induce positive intentions to act safe on the road for both pedestrians and motorists. Also, perceived personal control serves as a positive significant predictor of various safety-related motivations and intended behaviors. This research experimentally studied the differential effects of time horizon and regulatory focus framing on advancing traffic safety throughout effective messaging, an endeavor that shall benefit transportation authorities, city administrators, policymakers, and the general public. The tested message framing can be adopted in various forms, including text message, billboards, road signs, flyers, educational workshops, etc.
PI's Background: Dr. Aly Tawfik
Project's Start date: December, 2020
Project's End date: July, 2022
Abstract: Electric vehicles (EVs) are a valuable tool in addressing the climate and energy challenges placed on our transportation systems. However, while national and international market shares of EVs have been rising with exponential rates, access to EVs of low-income populations has been significantly slower. This research developed a business model for expanding the EV market to low-income Californians. The team developed the model from qualitative data from various stakeholders, including Electric and Solar Companies, Professional and Community-Based Organizations, State Agencies, research institutions, and more, which enabled insights regarding various barriers that hinder the adoption of EVs. The team also used a state-wide survey to understand the barriers from the point of view of lower income Californians. The business model created from this data can be used by state administrators, policy makers, and social emprises to mitigate the barriers faced by low-income Californians within the EV market.

PI's Background: Dr. Aly Tawfik
Project's date: December, 2022
Abstract: HSR is one of the largest projects in the nation currently under construction 24stations, 800 miles of rail from Sacramento to San Diego. HSR will impact travel accessibility between cities and areas across the state. Its objective is to Quantify and visualize the impact of HSR on travel time. Compare HSR to other travel modes (roads, bus, air and train) Provide more information to the public on whether investment is valuable. Completed with use of ArcGIS and advanced ArcGIS extensions including Network Analyst and Model Builder to produce: OD Matrices Isochrone Maps.
Report Coming Soon
PI's Background: Dr. Aly Tawfik
Project's date: December, 2021
Abstract: Many believe that telecommuting could be a solution for some of the significant adverse impacts of our transportation systems, e.g., traffic congestion, greenhouse gas and air pollution emissions, and energy consumption. Observations may have further strengthened this belief during the first year of the COVID-19 Pandemic when streets were deserted and clean air and wildlife returned to urban areas. Accordingly, this study investigates the legitimacy of this belief. Telecommuting is the Substitution for work regularly performed at the workplace with work at home or a location close to home. It can be performed multiple days per week, for full or partial days. A telecommute framework was adapted to analyze the 2017 National Household Travel Survey dataset. To study the impact of telecommuting, in its various forms, on daily trip counts and daily miles traveled; for urban and rural workers. The derived relationships would indicate if increased telecommuting, expected after the COVID-19 Pandemic, would result in fewer or greater trip counts and miles traveled in urban and rural contexts.
Report Coming Soon
Year 2 (2019)
PI's Background: Dr. Chih-Hao Wang
Project's Start date: May 1 2019
Project's End date: Dec 31 2019
Abstract: This research examines the accessibility to multi-use paths in a variety of neighborhoods in Fresno, California. This study aims to develop a multi-objective optimization modeling framework to be used by decision makers in transportation and policy to maximize the total accessibility to multi-use paths across the city while minimizing the gap between low- and high- accessibility neighborhoods by an optimal allocation of active transportation. Researchers calculate accessibility to multi-use paths by measuring the total length of multi-use paths (walkway and bikeway) a resident could reach from their own Census block group with a 30-minute cycling ride. The study employs a geographically weighted regression (GWR) model to capture the local relationships between accessibility to multi-use paths and previous transportation investments (walkways, bikeways, and primary and secondary roads), while controlling for other socioeconomic factors. The marginal-effect analysis for the GWR results categorizes the areas within Fresno into economically efficient, inefficient, and indifferent locations for further investments. The researchers embed the GWR results into a multi-objective optimization modeling framework to improve accessibility to multi-use paths over the city and simultaneously address inequality in active-transportation accessibility. This research provides decision makers with insight into the problem of making of an economically-efficient and socially-equal active transportation plan accessible to people from diverse backgrounds with the ultimate goal of fostering public health.
Project's Start date: May 1 2019
Project's End date: Dec 31 2019
Abstract: The goal of the “Fresno State Transportation Challenge” was outreach to schools and community engagement, to provide K-8 students opportunities to learn about transportation and transportation-related careers, and to practice 21st century skills by solving a transportation-related issue in their community. Through the pedagogical frameworks of action civics and eduScrum (a method to facilitate self-managed teamwork with a visual board), teachers and students worked on solving issues in their community. They learned design thinking to identify issues and develop solutions while using eduScrum to manage their work. University students from transportation engineering visited the schools regularly to support the K-8 students in their work on a transportation-related project. The study tested two different formats: summer school and during the regular academic school year. The research question was: What is the impact of the “Fresno State Transportation Challenge” on K-8 students, K-8 teachers, university students, and community members? The research methods involved observations, open interviews, and a final survey of participants. Key findings reveal the Transportation Challenge is suited to teach elementary and middle school students about transportation and transportation-related careers, and to encourage them to apply this knowledge in addressing a transportation-related issue in their community. The involvement of university students had a positive influence on the younger students’ learning in regard to motivation, role modeling, and broadening the perspective of transportation-related careers. The pedagogical approaches of action civics and eduScrum facilitated the development of career skills, such as collaboration, communication, creativity, teamwork, critical thinking, and persistence to overcome challenges. Implications for practice include that leveraging university resources, such as the Fresno State Transportation Institute, can be an effective way to engage K-8 students and teachers in transportation-related authentic learning experience, increase their awareness of transportation-related careers and topics, and develop their career skills.
PI's Background: Dr. John Walkup
Project's date: December, 2019
Abstract: This project proposed centers on developing a suite of standards-aligned, rigorous lesson plans for secondary school teachers centered on transportation issues. Each grade level will receive 3-4 lesson plans to cover a complete 2-week unit of study. Each grade level will address a specific major topic within the field of transportation. Examples of such topics will include the societal impact of autonomous vehicles, transportation safety, and traffic flow. The designers of this project believe that education on transportation issues from an early age can elevate awareness of these issues and boost interest in transportation careers. Each lesson plan will span at least one full classroom period; some will span multiple periods. Each lesson plan will be guided by a culminating activity and will include (a) the background knowledge that expected of students, (b) strategies for scaffolding students who do not possess this background knowledge, (c) the facts, skills, concepts, and metacognition address in the lesson plan, and (d) teaching methods likely to prove effective for delivering the lesson plan in the classroom.
PI's Background: Dr. Samer Sarofim
Project's Start date: April 1, 2019
Project's End date: December 31, 2019
Abstract: The ultimate objective of this research is to empirically investigate the differential effect of message framing on message recipients’ attitudes and intended behaviors related to pedestrian, cyclists, and motorists traffic safety practices. The framework empirically investigated time horizon (expansive vs. limited) and regulatory focus (prevention vs. promotion) message framing. The role of the individual difference of perceived personal control on the perceptions of the presented messages and behavioral intentions to adopt safety transportation practices was studied. Various messages are designed to employ a multilayer framing and fit with a 2 (time horizon: expansive vs. limited) x 2 (regulatory focus: promotion vs. prevention) between-subjects design. Findings suggest that the messages adopting expansive and promotion-focused framing combination seem to be more effective and has a higher tendency to induce positive intentions to act safe on the road for both pedestrians and motorists. Also, perceived personal control serves as a positive significant predictor of various safety related motivations and intended behaviors. This research experimentally studied the differential effects of time horizon and regulatory focus framing on advancing traffic safety throughout effective messaging, an endeavor that shall benefit the public, transportation authorities, city administrators, and policymakers.
PI's Background: Dr. Mazen Eldeeb
Project's Start date: 3/ 1/19
Project's End date: 12/31/19
Abstract: The study addresses two of the main challenges facing combustion modeling for transportation fuels: simultaneous simulation of non-related combustion problems and reducing the computational cost of the modeling process itself. To address the first challenge, researchers determine a characteristic flame time from thermal diffusivity and laminar burning velocity. Researchers examine parametric dependence of flame time and ignition delay time on pressure, temperature and equivalence ratio for methane, based on validated chemical kinetic mechanisms. The study reveals flame time and ignition delay time show similar temperature dependence, flame time has stronger dependence on equivalence ratio and weaker dependence on pressure than ignition delay time. The study also establishes a correlation to predict flame time, and subsequently, burning velocity, based on knowledge of the relevant auto ignition time. Differences between methane, propane and ethanol are also explored. Researchers address the second challenge in a chemical kinetic modeling study of the high-temperature ignition behavior of Tetrahydrofuran (THF), a promising second-generation transportation biofuel. The study implements a Stochastic Species Elimination (SSE) reduction approach to develop multiple skeletal versions of a detailed chemical kinetic model of THF from the literature based on ignition delay time simulations at various pressures and temperatures. The developed skeletal versions are combined into a global skeletal model. The study uses ignition delay time simulations using detailed and skeletal models, with good agreement observed at higher temperatures. Next, researchers use sensitivity analysis to identify the most important reactions responsible for the performance of the skeletal model. Finally, they perform reaction rate parameter modification for such reactions in order to improve the agreement of detailed and reduced model predictions with literature experimental ignition data. This work contributes toward improved understanding and modeling of the oxidation kinetics of conventional and bio-derived transportation biofuels, as well as the estimation of laminar burning velocity that can be encountered in turbulent combustion simulations. This would ultimately contribute into the design of cleaner and more efficient transportation systems, and support the testing and adoption of novel fuels as additives and/or replacement to conventional non-renewable fossil fuels.
PI's Background: Dr Hovannes Kulhandjian.
Project's Start date: 03 June, 2019
Project's End date: 27 December, 2019
Abstract: In this work, we developed a visible light communication (VLC) framework that can be used for Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS). ITS has been motivated by the need for reducing traffic congestion and offering better user experience in navigation and location-specific services. Recently, VLC has drawn a great deal of attention in the research community, including the development of new applications for ITS. It would be of great use to enable the traffic lights to be able to talk to the vehicles in their proximity and convey important information about the traffic condition. In this project, we developed a framework that can potentially support infrastructure-to-vehicle (I2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication. (In our context the infrastructure refers to traffic lights using VLC.) Specifically, traffic lights will be used to not only to order traffic flow, but also to share some important information to the cars. The developed smart traffic light system can provide information about the traffic conditions several blocks down the road and, in case of accidents, this information would be useful for the driver to detour their original route to help reduce congestion and save time. In order to do that we have developed a transmitter circuitry that is composed of an embedded system and optical electronics. In addition, we have developed the receiver circuitry in which the photodiode along with other circuitry is used for detecting and decoding the VLC signal coming from the traffic lights. We have also developed and experimented in a laboratory with a novel optical code-division multiple-access (CDMA) scheme for overloaded optical CDMA transmission in which the optical codes are uniquely decodable. This new coding system could potentially provide higher data rate in the VLC protocol establishment.
Project's Start date: May, 01, 2019
Project's End date: December 31, 2019
Abstract: Research on the relationship between urbanicity and physical activity yielded mixed results despite many studies consistently showing that residents tended to undertake more transportation-related physical activity in a more urban environment. This study analyzed the 2017 NHTS data to examine the geographic disparities in physical activity, particularly transportation-related physical activity in the United States. Our analysis suggests the relationship between urbanicity and physical activity demonstrates a flat U- shape in graphed data. Residents are more physically active when they live in the areas from the two ends of the urbanization spectrum: inner cities and inner suburbs of large metropolitan areas and the rural parts of non-metropolitan areas. Suburbanites, particularly mid-ring and outer-ring suburbanites walk the least. Only very slight geographic variation exists in the weekly rates of walk and bike trips that are strictly for exercise. The study revealed greater variation of the weekly rates of walk and bike trips that are for non-exercise purposes. This study suggests a more complicated relationship between urbanicity, active travel, and physical activity in a broader geographic context. More research needs to examine whether and how new urbanist design can promote active travel, particularly active travel strictly for exercise, in rural areas and areas of low urbanicity.
PI's Background: Dr. Shahab Tayeb
Project's date: December, 2019
Abstract: The Internet of Vehicles (IoV) aims to establish a network of autonomous and connected vehicles that communicate with one another through facilitation led by road-side units (RSUs) and a central trust authority (TA). Messages must be efficiently and securely disseminated to conserve resources and preserve network security. Currently, research in this area lacks consensus about security schemes and methods of disseminating messages. Furthermore, a current deficiency of information regarding resource optimization prevents further efficient development of this network. This paper takes an interdisciplinary approach to these issues by merging both cybersecurity and data science to optimize and secure the network. The proposed method is to apply Prim’s algorithm to an existing vehicular security scheme, Privacy-Preserving Dual Authentication Scheme (PPDAS), to further network efficiency in terms of power and time consumption. When a dual authentication security scheme is in place, the time taken for message dissemination follows a quadratic growth; applying Prim’s algorithm to the security scheme reduces the time to disseminate messages to a linear growth. The number of messages sent was decreased by a magnitude of up to 44.57. Contemporary security schemes are compared with PPDAS to justify the overhead consumption. Through the proposed approach, the usage of network resources, such as power and time, is reduced, which substantially enhances the performance of the vehicular network and allows for the scalability of the IoV.
PI's Background: Mr. Malshana Wadugurunnehalage
Advisor's Background: Dr. Ajith Weerasinghe
Project's Start date: March 4th, 2019
Project's End date: December 31, 2019
Abstract: This project has three main objectives. The first objective is standardizing battery. There are various types of batteries used in the Automotive Industry. When this comes to Electric Vehicles (EV), battery manufacturers are hiding different recipes that they use for manufacturing batteries. This creates numerous limitations, especially in recycling processes and growth of EV demand. In this project, the importance of standardizing on EV battery technologies are discussed. The second objective is exploring battery switching stations. Battery Switching is identified as a promising technique for secure charging and a better way of maintaining the entire EV battery system in a region. In this project, it's identified the importance of having switching stations instead of fast charging. Fast charging leads to battery degradation and its effects on the grid if the power supply is not properly maintained. Considering tremendous benefits, implementing switching stations are widely encouraged throughout this project. The third objective is exploring IoT(Internet of Things) for efficient green energy transportation. Currently, the Internet plays a vital role in the business world. Through the IoT concept, it creates the connection between Electric Vehicles, Switching Stations, and other private and government organizations which interested to access the relevant data. In this way, it’s expected to energize the total battery switching system, bringing more productive and effective by establishing a robust IoT system. In addition to that, ultimately it's expected to make possible pathways to enhance performances of Electric Vehicles in public transportation.
This project aims to demonstrate the possible pathways to implement battery switching approaches for Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV) through the Electric Vehicle (EV) battery standardizing. During the past decade, there was significant interest in EVs and their technologies. Due to the number of studies and experiments which carried out for enhancing total performances of EVs, demand a different type of EVs are grown faster. The growth of different battery technologies has led to improving the primary aspects of Electric Vehicles. As a result of relentless research and developments regarding different battery technologies, the distance travel per single charge was growing day by day. Battery design and manufacturing techniques becoming complex, and battery manufacturers tend to hide their battery chemistry intend to increase the performance of their product stay strong in the competition.
EV batteries carry a different kind of chemical which can be harmful to the environment. Properly managed recycling approaches are essential to establish and maintain robust operation due to the increasing usage of EV batteries. Hiding their recipes of battery manufacturing, create complexity on the recycling process and through the enforcement of established rules and regulations for EV battery standardizing, battery manufacturers will be more open with their manufacturing techniques. Through this project, environmental impact due to increasing usage of EV batteries and possible pathways to create new businesses through recycling will be discussed. EV battery standardizing becoming an important concept, and scientists and engineers are found possible pathways to implement other approaches to establish a different type of business model through the EV battery standardizing. Battery switching stations are one of the promising business models, been introduced and, through this project, the values of such a business model will be discussed.
Throughout the project, battery switching stations are identified as the most important aspect of harvesting benefits from all around. To make this battery switching process more effective and efficient, Introducing of the Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the major aspects of this project. The suggested network is something that goes beyond the traditional data acquisition and performance monitoring system. Through this system, the vehicle driver, the staff of battery switching station and data center for performance monitoring and system development, will be aware of each and every switched battery. This system will be demonstrated throughout the project and advances will be highlighted. In this way, there are numerous benefits that will be demonstrated and discussed throughout the project. Though it will be a time-constrained project, in the beginning, the further developments will be discussed at the end of the project. Depending on the availability of time and funds, this project will be continued for developing further, meeting its’ all aspects.
Report Coming Soon
Year 1 (2018)
PI's Background: Dr. Nancy Van Leuven
Project's Start date: 1 July, 2018
Project's End date: 31 December, 2018
Abstract: Over the past few years, there have been notable trends in the areas of tracking public opinion, especially in public issues such as transportation. Such powerful processes continue to be a critical (and often mandated) component of the democratic process as they help policy makers connect with affected constituencies. This study explores travel trends and transportation preferences of a sample of adults in the California Central Valley of Fresno, an increasingly congested region that is also heavily agricultural and regarded as an expected launching pad for California’s first high- speed rail system. Relying on an e-survey modeled off a statewide polling project, this study used a modified electronic survey as a valuable predictor of public opinion. Findings include preferences skewing toward concern about local issues (road conditions, safety, accessible active transport) and a lack of knowledge about future mobility options (high- speed rail, driverless cars). Based on these results, Fresno should be viewed as a prime area for focused public information campaigns to foster behavior change and attitudes about potential transportation improvements.
PI's Background: Dr. Aly Tawfik
Project's Start date: December 2018
Abstract: Existing costs show that on average, Americans are spending approximately $.54 per mile for driving individually- owned (IO) vehicles. This value is based on factors such as fuel, maintenance, insurance, registration, parking, tolls and depreciation. Many of these factors will be affected with the arrival of autonomous vehicles (AVs) and more specifically, Shared Autonomous Vehicle (SAV) systems. For the purposes of realizing the advantages of future AVs and SAVs, a better understanding of future costs of travel is necessary. The goal of this research work is to estimate future travel costs using each of the AV and SAV Systems. These cost estimates would be crucial in evaluating the impacts of these technologies on future mobility and society. For this purpose, extensive literature reviews were conducted and a model was developed to analyze and evaluate the future travel costs using each of the AV and SAV systems. Results of this work indicate that future travel costs using SAV systems are likely to be substantially lower than those of using AV systems. This may lead to a disruption that can ultimately influence consumers to switch from owning a vehicle to on- demand mobility services.
PI's Background: Dr. Douglas Singleton
Project's Start date: December, 2018
Abstract: This research focused on developing a suite of standards-aligned, rigorous lesson plans for secondary school teachers centered on transportation issues. The first phase of the grant project focused on training a cadre of prospective K-12 secondary school teachers to develop rigorous, standards-aligned lesson plans. Six students were recruited from across multiple disciplines including the liberal arts, physics, geology, and science education. Results of the training were strongly positive as indicated by post-training anonymous survey results. During the second phase, students developed a total of 19 lesson plans. Examples of such topics include the societal impact of autonomous vehicles, transportation safety, and traffic flow.
PI's Background: Dr. Maryam Nazari
Project's Start date: 16 June, 2018
Project's End date: 31 December, 2018
Abstract: Application of Tire-Derived Aggregates (TDA) as a green, durable, and economically-efficient material, enhances the sustainability of transportation infrastructure. Throughout the course of this research study, the application of TDA in combination with expanded clay (EC) aggregates will be investigated in concrete slabs used in road pavements and bridge decks serving nonauto traffic, such as bicycle routes, through a set of experimental tests and life-cycle cost analyses. To this end, TDA, which is obtained from recycled tires, and EC, produced in rotary kilns, substitute coarse aggregates in conventional concrete. The final product, also known as lightweight rubberized concrete, is durable and economically-efficient. It also enhances the sustainability of transportation infrastructure by mitigating the necessary maintenance and rehabilitation needs of these slabs. In this report, an experimental study has been undertaken to first estimate mechanical properties of lightweight rubberized concrete using 100% EC, 100% TDA, and a mixture of 20% EC – 80% TDA; the TDA was replaced by the volume of the EC aggregates. Next, a series of static flexural and dynamic impact-fatigue tests were performed on simply-supported beam specimens and slab assemblies, respectively, to measure both modulus of rupture and durability when subjected to the applied loads. The cyclic testing results confirmed a lower flexural strength of the rubberized concrete specimens. However, the specimens exhibited an ability to withstand larger plastic deformations up until the point of failure. Using the results of impact-fatigue tests, a life- cycle cost analysis was also performed, which confirmed long-term benefits of constructing green and durable infrastructure, using TDA and EC, on transportation investments. In conclusion, using these durable materials in infrastructural construction will lessen their maintenance and rehabilitation needs. Further, this application will divert waste tires from landfills.
PI's Background: Dr. Yushin Ahn
Project's Start date: 16 June, 2018
Project's End date: 31 December, 2018
Abstract: Monitoring the health of bridges uses various sensors and techniques and provides quantitative and reliable data on the condition of bridges. Among measurable quantities, vibration induced by traffic loads has been known as a good indicator of the condition of bridges, serviceability to pedestrians, fatigue analysis, etc. Here we use non-metric, off-the- shelf, Digital Single-Lens Reflex camera (DSLR) as a sensor and apply a photogrammetric approach to measure three bridges live load traffic vibration. We first tested our approach with shake-table equipment and showed the reliability of the methodology we use through measuring magnitude and frequency of the shake-table, which was then applied to two highway and one local bridges. The results show that vibrational magnitudes are well within the design recommendations of the American Association of State highway Transportation (AASHTO) and that frequencies are in the range of similar bridges that previously published. Furthermore, by providing velocity and acceleration computed from camera derived displacement, we showed that the proposed method is cost-effective and feasible as well as having a good potential for bridge health monitoring.
PI's Background: Dr. Xiaojun Li
Project's Start date: December 31, 2019
Project's End date: March 1, 2020
Abstract: Each year, about 122 million tons of aggregates, a major structural component of pavement, are used in asphaltic mixtures in pavement construction. At the same time, aging U.S. infrastructure produces around 200 million tons of demolition waste each year, half of which is concrete debris. Therefore, introducing recycled concrete aggregate (RCA) as hot mix asphalt (HMA) aggregate could not only relieve the disposal pressure but also result in considerable reductions in cost, energy usage, and greenhouse gas emissions in the paving industry.
A limited number of studies regarding the use of RCA to substitute virgin aggregate
in HMA (RCA-HMA) exist. More importantly, the findings reveal discrepant or even contradictory
results, regarding the effects of RCA on almost all the volumetrics and performance
indicators of RCA-HMA. Because RCA is different from virgin aggregate, as RCA particles
are at least partially covered by a residual cement mortar (RCM) layer, the attached
RCM in RCAs from different concrete sources could significantly differ in terms of
content, porosity, and distribution on the RCA surface.
This study aims to determine the characteristics of RCA and RCM, such as RCM content,
specific gravity, and absorption, and to evaluate their effects on the volumetrics
and performance indicators of RCA-HMA. This research evaluates the variation in the
properties of RCA and RCM obtained from different sources and their effects on RCA-HMA’s
performance. The research revealed the properties of RCA from different sources vary
significantly. It is insufficient to predict the volumetrics and performance of RCA-HMA
using only the information of RCA, such as RCA replacement rate and gradation. Information
pertaining to the RCM’s properties, such as the RCM content, specific gravity, and
absorption, is critical for the prediction of the RCA-HMA properties, including optimum
binder content (OBC), voids in mineral aggregate (VMA), voids filled with asphalt
(VFA), resistance to permanent deformation, and moisture damage susceptibility. The
results of this investigation can help to ensure reliable performance of RCA-HMA in
practice by controlling the properties of RCM in the RCA.
PI's Background: Dr. Chih-Hao Wang
Project's Start date: March 1, 2019
Project's End date: December 31, 2019
Abstract: Fresno has been regarded as a city with a high concentration of poverty. There-fore, it is extremely important to examine whether transportation inequality exists in Fresno because transportation shapes residents’ economic opportunities, physical activities and social interactions. This study is to address this issue by looking at whether a resident of Fresno would have an equal opportunity to ac-cess to a variety of urban opportunities, such as jobs, physical activities and din-ing, social interactions, and public facilities. Two non-auto (green) transportation modes (i.e. public transit and cycling) are considered in this study since not eve-ryone can afford for a private vehicle. We fist use the GIS (Geographic Infor-mation System) to illustrate the service area by using these two green transporta-tion modes, respectively, for each block group in the city. With the recently com-pleted “open street” data, we then use the service area to count the number of various urban opportunities (jobs, restaurants, parks, multi-use paths, schools, libraries, and schools) that a block group can reach within a 10-, 20-, 30-, 45-, and 60- minute-long travel time by transit or cycling. This is based on the will-known cumulative opportunity approach to measure the accessibility of a com-munity to various opportunities in a city. To examine whether there exist differ-ence in accessibility between a community and one another, we compare an ar-ray of computed accessibilities between better-off communities and worse-off ones. Several economic and social-demographical factors are considered to di-vide the communities into two groups, including income, property value, school enrollment, vehicle ownerships, race, and age. This would allow for a more com-prehensive way to compare the accessibility for many socioeconomic aspects. Another innovation in this study is to create a platform to flexibly group communi-ties into two for the accessibility comparison. This would reveal whether the re-sults are sensitive to the threshold used for grouping. The comparison results suggest that the current green transportation network do help with the accessibil-ity in terms of economic opportunities for economically disadvantaged neighbor-hoods. However, the city might need to focus on improving the efficiency of the bus system to provide a wider service area for more urban opportunities. Stu-dents might be a good target for further study to better understand their needs because there is no consistent patterns found from the results. Finally, the find-ings point out that more efforts on providing multi-use paths need to be done to improve the accessibility by cycling for non-white and adolescent groups.
PI's Background: Dr. Christian Wandeler
Project's Start date: March 1, 2019
Project's End date: October 31, 2019
Abstract: The complexity of a globalized world, accelerating technological advances, and rapid change challenge educational systems. Around the world the call is to develop 21st century skills with a focus on career readiness, ability for lifelong learning, and collaboration skills. The development of the foundational elements of civic engagement (civic knowledge, skills, and dispositions) of children and youth is also a dominant concern for educators and policymakers. Unfortunately, not all youth have the same opportunities to develop civic self-efficacy. However, the civic empowerment engagement gap can be closed by providing underserved students with interactive and authentic civic experiences.
We strove to create such an authentic civic experience and piloted the Fresno State Transportation Challenge (FSTI) at an elementary school in the Washington Unified School district, Fresno County, California. The research question for this innovation grant was: Can we leverage the expertise and resources of the Fresno State Transportation Institute to bring high quality educational experience to underserved students and help them improve their communities?